| Polynomial and/or
polynomial functions and equations
|
| A polynomial (in a variable
x) is a function or an expression written
in standard form
|
| f (x) = anxn
+ an -1xn
-1
+ an -2xn
-2
+ . . . + a2x2
+ a1x + a0 |
| where,
an,
an -1,
. . . , a2,
a1,
a0
are real numbers called coefficients. If an
is non-zero, polynomial is of degree n
(n is a natural
number).
|
|
Addition and subtraction of polynomials
|
| If
g (x)
= bmxm + bm -1xm
-1
+ . . . + b2x2
+ b1x + b0
then for m = n, |
| f
(x) + g (x) = (an
+ bn)xn
+ (an
-1
+ bn
-1)xn
-1
+ . . . + (a2
+ b2)x2
+ (a1
+ b1)x
+ (a0
+ b0) |
|
Example:
Given f
(x) = -
x3 + 2x2
-
3x + 1
and g
(x) = 2x4 -
5x3 + x -
4 then |
| f
(x) -
g (x)
= (0 -
2)x4 + (-1
-
5)x3 + (2 -
0)x2 + (-
3 -
1)x + (1 + 4) |
|
= -
2x4 + 4x3
+ 2x2 -
4x + 5 |
| Multiplication
of polynomials
|
|
We multiply polynomials using the distributive law and the commutative
and associative laws of multiplication and addition.
|
|
Example:
Given are polynomials, f
(x) = -
2x3 + 4x -
1 and
g
(x) = x2 + 3x
-
4 then |
|
f (x)
×
g (x)
= (-
2x3 + 4x -
1) ×
(x2
+ 3x -
4) |
|
= -
2x5 + 4x3
-
x2 -
6x4 + 12x2
-
3x +
8x3
-
16x + 4 |
|
= -
2x5 -
6x4 + 12x3
+ 11x2 -
19x + 4 |
|
| Division
of polynomials
|
| Dividing two polynomials,
p (x)
and q
(x),
obtained is quotient Q
(x) and
remainder R
(x)
related by |
| p
(x) = Q (x) ×
q (x)
+ R (x). |
| The two
polynomials are divisible if
R (x)
= 0. |
|
|
Example: Given,
f
(x) = 3x3 -
10x2 + 11x -
4 and g
(x) = x2 -
2x + 1, find
Q
(x) = f (x) ¸
g (x). |
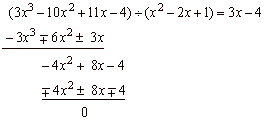 |
| therefore,
3x3 -
10x2 + 11x -
4 = (3x
-
4) ×
(x2 -
2x + 1)
and R
(x) = 0. |
|
|
Example:
Given, f
(x) = x3 + 2x and g
(x) = -
x2 + x + 1,
find quotient
f (x) ¸
g (x). |
 |
| thus,
x3
+ 2x =
(-
x -
1) ×
( -
x2 + x + 1) +
4x + 1
i.e., Q
(x) = -
x -
1 and R
(x) = 4x + 1. |
|