| |
|
|
Rectangular
(Two-dimensional, Cartesian) Coordinate System |
 The
area
of a triangle
The
area
of a triangle |
 The
coordinates of the centroid of a triangle
The
coordinates of the centroid of a triangle |
 Lines
parallel to the axes, horizontal and vertical lines
Lines
parallel to the axes, horizontal and vertical lines
|
|
|
Polar Coordinate System
|
 Polar
and Cartesian coordinates relations
Polar
and Cartesian coordinates relations |
|
Conversion from polar
to rectangular coordinates |
|
Conversion from
rectangular to polar coordinates |
 Polar coordinates of a point
Polar coordinates of a point |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The
area
of a triangle |
| The
rectangular coordinates of three points in a coordinate plane
describe a triangle. Using given coordinates we derive the
formula for the area of the triangle, as is shown in the diagram
below. |
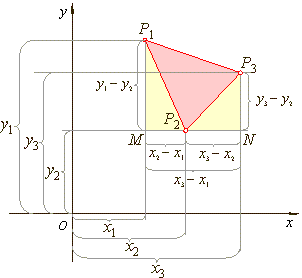 |
| The
area of the given triangle P1P2P3
equals |
| the
area of the trapezium P1MNP3
minus
the |
| sum
of the areas of the right triangles, P1MP2
and |
| P2NP3,
that is |
| PD =
1/2·[(y1 -
y2)
+ (y3 -
y2)]
· (x3 -
x1)
- |
| -
1/2·[(y1
- y2)·(x2
- x1)
+ (y3 -
y2)·(x3
- x2)] |
| which
after simplifying and rearranging gives |
| PD=1/2·[x1(y2
- y3)
+ x2(y3 -
y1)
+ x3(y1 -
y2)] |
|
|
|
| Example:
Two vertices of a triangle
lie at points A(-4,
0)
and B(5, -2)
while third vertex C
lies on the y-axis.
Find the coordinates of the point C
if the area of the triangle is 31 square units. |
| Solution: |
|
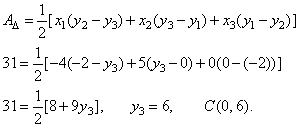 |
|
|
|
|
|
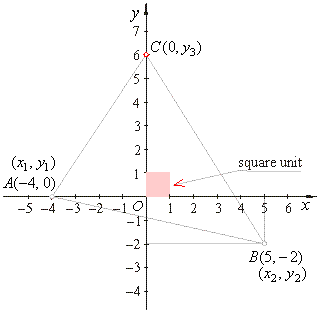 |
|
|
| The
coordinates of the centroid of a triangle |
| The
point of coincidence of the medians of a triangle is called the centroid. |
| The
median is a straight line joining one vertex of a triangle to
the midpoint of the opposite side and divides the triangle into
two equal areas. |
| The
centroid cuts every median in the ratio 2
: 1 from a vertex to the
midpoint of the opposite side. |
| The
coordinates of the centroid of a triangle given its three
points, P1, P2 and
P3
in a coordinate plane: |
| The
centroid M(x,
y),
where |
x
= 1/3 · (x1 + x2
+ x3), y =
1/3 · (y1
+ y2
+ y3) |
|
|
|
| Lines
parallel to the axes, horizontal and vertical lines
|
| If
the y
value never changes, i.e., if it takes the same constant value
y =
c
a line is parallel to the
x-axis
and is called a horizontal line (or constant). |
| If
the x
value never changes, i.e., if it takes the same constant value
x
=
c a line is parallel to the y-axis
and is called a vertical line. |
|
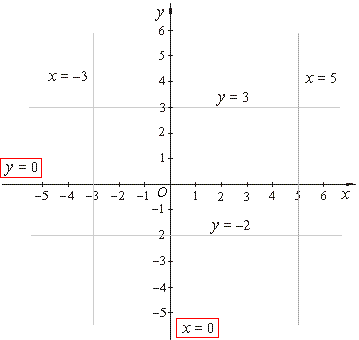 |
|
|
Polar coordinate system
|
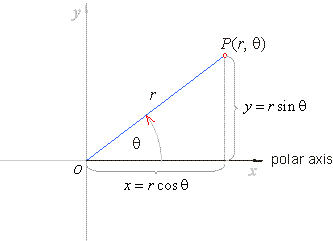
| The
polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system
in which each point P
on a plane is determined by the length of its position vector r
and the angle q
between it and the positive direction of the x-axis,
where 0 <
r
< + oo
and 0
<
q
< 2p. |
 |
|
| Polar
and Cartesian coordinates relations, |
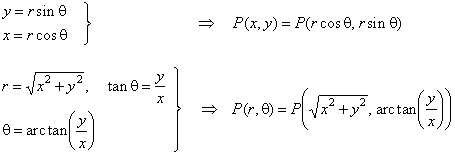 |
| Note,
since the inverse tangent function (arctan or tan-1)
returns values in the range -p/2
< q <
p/2, then |
|
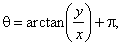
for points lying in the 2nd or 3rd quadrant |
 |
|
|
and for points lying in the 4th quadrant |
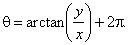 |
|
|
| Example:
Convert Cartesian coordinates
(-1,
-Ö3)
to polar coordinates. |
| Solution: |
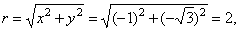 |
|
and since the point lies in the 3rd quadrant,
then |
|
 |
|
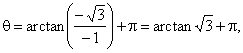 |
|
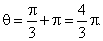 |
|
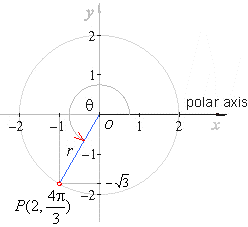 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
College
algebra contents A
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |