|
|
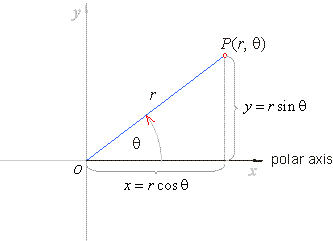
Polar coordinate system
|
| The
polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system
in which each point P
on a plane is determined by the length of its position vector r
and the angle q
between it and the positive direction of the x-axis,
where 0 <
r
< + oo
and 0
<
q
< 2p. |
 |
|
| Polar
and Cartesian coordinates relations, |
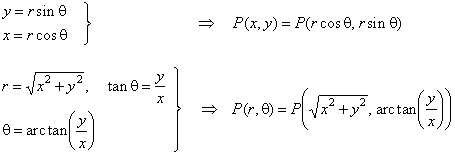 |
| Note,
since the inverse tangent function (arctan or tan-1)
returns values in the range -p/2
< q <
p/2, then |
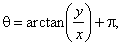
|
for points lying in the 2nd or 3rd quadrant |
 |
|
|
and for points lying in the 4th quadrant |
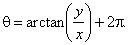 |
|
|
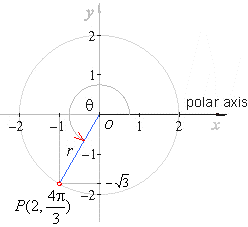
| Example:
Convert Cartesian coordinates
(-1,
-Ö3)
to polar coordinates. |
| Solution: |
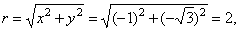 |
|
and since the point lies in the 3rd quadrant,
then |
|
 |
|
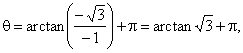 |
|
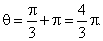 |
|
 |
|
|
| Equation
of a line in polar form |
| Lines
parallel to the axes, horizontal and vertical lines |
| Lines
parallel to the y-axis |
| A
vertical line, x
=
c is
represented by the equation |
| r
cosq
=
c
or |
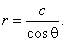 |
|
|
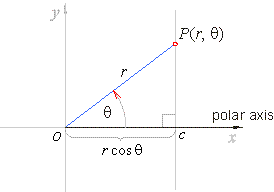 |
|
| Lines
parallel to the x-axis |
| A
horizontal line, y
=
c is
represented by the equation |
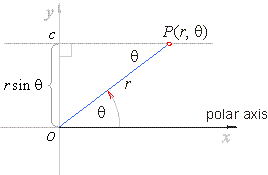
| r
sinq
=
c
or |
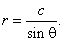 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| Lines
running through the origin or pole (radial lines) |
| The
equation of a line through the origin or pole that makes an angle
a with the positive
x-axis |
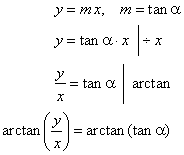 |
| is
represented by the equation |
q
=
a |
in polar coordinates. |
|
|
| Polar
equation
of a line |
| As |
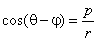 |
|
|
| the
polar equation of a line |
|
|
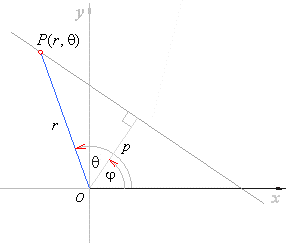
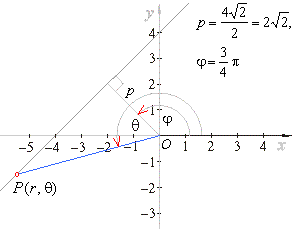
| where
p
is the distance of the line from the pole O
and j
is the angle that the segment p
makes with the polar axis. |
|
 |
|
|
| Example:
Write polar equation of the
line passing through points (-4,
0)
and (0, 4). |
| Solution:
Using polar equation of a line |
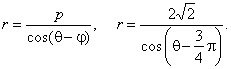 |
| Proof,
use of Cartesian to polar
conversion formulas. |
| The
intercept form of the line |
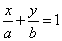 |
or |
|
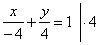 |
| -x
+ y =
4,
y
=
x
+ 4 |
|
 |
|
|
-r
cosq
+ r sinq
=
4,
r (sinq
-
cosq
)
=
4, |
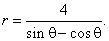 |
|
|
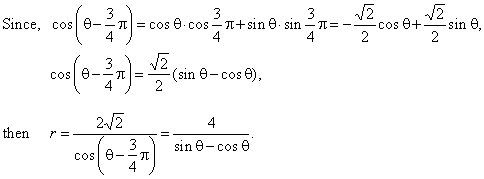 |
|
| Equation
of a circle in polar form |
| General
equation of a circle in polar coordinates |
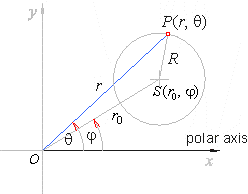
| The
general equation of a circle with a center
at |
| (r0,
j)
and radius R. |
| Using
the law of cosine, |
|
r2
+ r02
-
2rr0
cos(q
-
j)
=
R2 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| Polar
equation of a circle with a center on the polar axis running
through the pole |
| Polar
equation of a circle with radius R
and a center on the polar axis running through the pole O
(origin). |
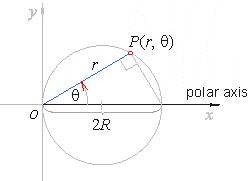
| Since |
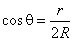 |
then, |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| Polar
equation of a circle with a center at the pole |
| Since,
r2
=
x2
+ y2 and
x2
+ y2
=
R2 then |
r
=
R |
|
|
| is
polar
equation of a circle with radius R
and a center at the pole (origin). |
|
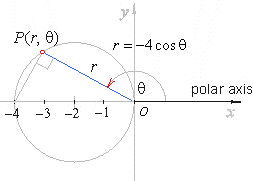
| Example:
Convert the polar
equation of a circle r
=
-4
cosq
into Cartesian coordinates. |
| Solution:
As, r
=
-4
cosq |
|
then r2
=
-4r
cosq, |
| and
by using polar to Cartesian conversion formulas, r2
=
x2
+ y2 and
x
=
r cosq |
| obtained
is
x2
+ y2
=
-4x |
|
x2
+ 4x
+ y2
= 0
|
|
or
(x
+ 2)2 + y2
= 4
|
|
the
equation of a circle with radius R
= 2 and
the
|
|
center
(-2,
0).
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|