|
| Ratios and Proportions
|
|
|
 Ratio
Ratio
|
 Proportion
Proportion
|
 Ratios
and proportion properties
Ratios
and proportion properties
|
 Direct proportion
Direct proportion
|
 Cross product, means and extremes
Cross product, means and extremes
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Ratio |
| A ratio is a comparison of two similar quantities obtained by dividing
one quantity by the other. |
| A ratio can be written as,
a
:
b
or as a fraction a/b
or by the phrase ' a to
b '. |
| A ratio is a way in which
quantities can be divided or shared. It shows how much bigger one
thing is than
another. |
| Make
the numbers in ratios smaller so that they are easier to
compare. Do this by dividing each side of the ratio
by the same number, the highest common factor. |
|
| Proportion |
| A proportion is
a statement of the equality of two ratios. If the fractions both reduce
to the same value, the proportion is true. |
| Example: |
|
9
: 6 = 3/2
and, 21
: 14 = 3/2,
follows,
9 :
6 = 21 : 14. |
|
|
| Ratios and proportion properties
|
| A ratio's value is not altered if both the first and second term are
multiplied or divided by the same number different from zero. |
|
a
:
b =
(a · c)
:
(b ·
c) |
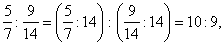 |
|
| |
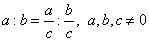 |
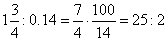 |
|
|
|
| Two quantities are in
direct proportion when they increase or decrease in the same ratio. |
|
| When two ratios are equal, then the
cross products of the ratios are equal. |
|
That is, |
a
:
b = c
:
d |
or |
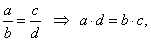 |
|
|
| the
product of the means is equal to the product of the extremes.
|
| The
first and last term in a proportion are called the extremes, the
second and third terms are called the means.
|
| If any three terms in
a proportion are given, the fourth may be found. |
| |
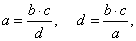 |
|
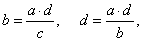 |
|
| |
the
extremes |
|
the
means |
|
|
|
| Examples: |
a)
2
:
x =
6 :
15 |
|
b)
8
:
(x
-
1)
= 2 :
7 |
|
c)
(7
-
x)
:
3 =
4x :
9 |
| |
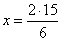 |
|
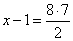 |
|
9 · (7
-
x) =
3 ·
4x |
| |
|
|
63
-
9x
= 12x |
| |
x = 5 |
|
x = 29 |
|
21x = 63
| ¸
21 |
| |
|
|
|
|
x = 3 |
|
|
| The first and third terms, and the second and the fourth terms in a
proportion are the corresponding terms. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |