|
|
|
|
Integral
calculus
|
|
|
|
Calculating
a definite integral from the definition examples
|
| Example:
Evaluate |
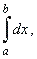 |
where f (x)
=
1, using the
definition of the definite integral. |
|
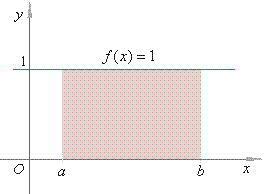
| Solution: Since
the graph of the constant f (x)
=
1
is the line passing through the point (0,
1)
parallel |
| to
the x-axis,
the region under the graph is the rectangle of base
=
(b
-
a)
with the height h
=
1. |
| Thus,
the area |
| A
=
(b
-
a) · 1
=
b
-
a, |
| as
shows the right figure. Therefore, |
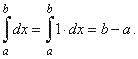 |
|
 |
|
|
| Example:
Evaluate
|
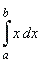 |
where f (x)
=
x, using the
definition of the definite integral. |
|
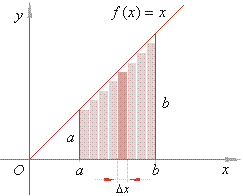
| Solution: Since
the graph of f (x)
=
x
is the line through the origin, coordinates of every its point y
=
x,
so
the region under the graph is the trapezium
with the height
b
-
a
and whose parallel sides are
a
and b.
Let's
use the partition of the interval [a,
b] into n
equal subintervals,
so that Dx
=
(b
-
a) / n
and |
| calculate
the
lower sum s
of inscribed rectangles, as
shows the right figure.
If
we choose the point xi'
to be the left-hand end of each
subinterval,
then |
| x1'
=
a
and
f (x1'
)
=
a |
| x2'
=
a
+
Dx,
f (x2'
)
=
a
+
Dx |
| x3'
=
a
+
2Dx,
f (x3'
)
=
a
+
2Dx |
|
·
· ·
·
· · |
| xn'
=
a
+
(n
-
1)Dx,
f (xn'
)
=
a
+
(n
-
1)Dx. |
|
 |
|
| We
use the Riemann sum to calculate the sum of inscribed rectangles with
bases of the same length, |
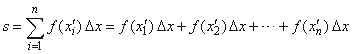 |
|
therefore,
s
=
a
Dx
+
(a
+
Dx)Dx
+
(a
+
2Dx)Dx
+
·
· ·
+
[a
+
(n
-
1)Dx]Dx |
|
s
=
Dx[n
a +
Dx(1
+
2
+
·
· ·
+
(n
-
1))] |
| to
calculate the sum of natural numbers inside of square brackets we use
the formula |
|
Sn
= [2a1 + (n -
1)d] for the sum of the
arithmetic sequence whose first term a1
= 1 and difference d
= 1, so
we get the sum equals
(n
-
1)n
/ 2, and since Dx
=
(b
-
a) / n
then, |
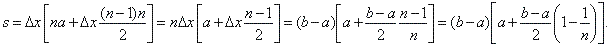 |
| Thus
the area under the graph of f (x)
=
x
over the interval [a,
b] |
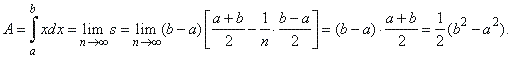 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents
L
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved.
|
|
|