|
Trigonometric
(cyclometric) functions and inverse trigonometric functions (arc
functions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Algebraic
and transcendental functions |
| Elementary
functions are, Algebraic functions
and Transcendental functions |
| Algebraic
functions |
|
· The
polynomial function
f (x) =
y = anxn
+ an-1xn-1
+ an-2xn-2
+
. . . +
a2x2
+
a1x + a0 |
|
y
=
a1x
+ a0
- Linear
function |
|
y
=
a2x2
+
a1x + a0
-
Quadratic
function |
|
y
=
a3x3
+
a2x2
+
a1x + a0
-
Cubic
function |
|
y
=
a4x4
+
a3x3
+
a2x2
+
a1x + a0
-
Quartic
function |
|
y
=
a5x5
+
a4x4
+
a3x3
+
a2x2
+
a1x + a0
-
Quintic
function |
|
- - - -
- - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - |
| ·
Rational
functions
- a ratio of two polynomials |
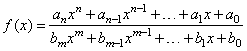 |
|
-
Reciprocal function |
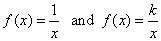 |
| |
-
Translation of the reciprocal function,
called linear rational function. |
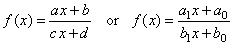 |
|
|
| Transcendental
functions - The
graphs of transcendental functions |
|
· Exponential
and logarithmic functions are mutually inverse functions |
|
- Exponential
function |
y
= ex
<=>
x = ln y,
e = 2.718281828...the
base of the natural logarithm, |
| |
exponential
function is inverse
of the natural logarithm
function, so that eln
x = x. |
|
- Logarithmic
function |
y
= ln x
= loge x
<=>
x = e y,
where x
> 0
|
| |
the
natural logarithm
function is inverse
of the exponential
function, so that
ln(ex) =
x. |
|
|
|
|
- Exponential
function |
y =
ax
<=>
x = loga
y,
where a > 0 and
a
is
not 1 |
| |
| exponential
function with base a is
inverse of the logarithmic
function, so that |
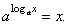 |
|
|
- Logarithmic
function |
y =
loga
x
<=>
x = a y,
where a
> 0,
a
is
not 1
and x
> 0 |
| |
the
logarithmic
function with base a
is inverse of the exponential
function, so that
loga (ax) =
x. |
|
|
| The
graph of the exponential
function y
= ax = ebx,
a
> 0
and b
= ln a |
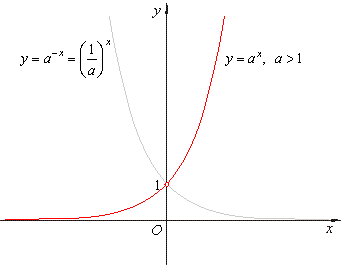 |
| The
exponential
function is
inverse of the logarithmic
function since its
domain and the range are respectively the range and domain of
the
logarithmic
function and |
| f
(f
-1(x))
= x that
is, f (f
-1(x))
= f (ax)
= loga (ax) =
x. |
|
| The
graph of the logarithmic
function y
= logax,
a
> 0
and for a
= e,
y
= logex = ln x |
 |
| The
logarithmic
function is
inverse of the exponential
function since its
domain and the range are respectively the range and domain of
the
exponential function and |
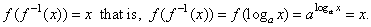 |
|
|
·
Trigonometric
(cyclometric) functions and inverse trigonometric functions (arc
functions) |
|
Trigonometric functions are defined as the ratios of the sides of a right
triangle containing the angle equal to the argument of the
function in radians.
|
| Or
more generally for real arguments, trigonometric
functions are defined in terms of the coordinates of the
terminal point Q of
the arc
(or angle) of the unit circle with the initial point at P(1,
0). |
|
|
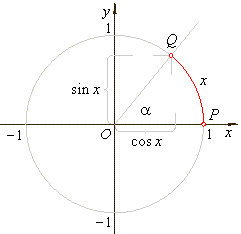 |
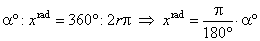 |
| sin2x
+ cos2x
= 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|