|
|
|
|
Imaginary
and Complex Numbers |
 Polar or trigonometric
notation of complex numbers
Polar or trigonometric
notation of complex numbers |
 Eulerís formula,
relationship between trigonometric functions and the complex exponential
function
Eulerís formula,
relationship between trigonometric functions and the complex exponential
function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Polar or trigonometric
notation of complex numbers |
| A point (x,
y)
of the complex plane that represents the complex number z
can also be specified by its distance r
from the origin and the angle j
between the line joining the point to the origin and the
positive x-axis. |
| Cartesian
coordinates expressed by polar coordinates: |
| x
= r cosj |
| y
= r sinj |
| plugged
into z
= x
+
yi
give |
|
z
= r
(cosj
+
isinj), |
|
| where |
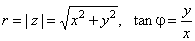 |
|
|
|
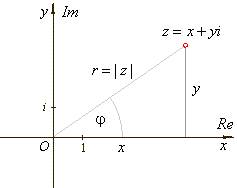 |
|
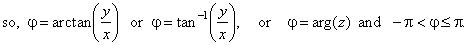 |
| Thus,
obtained is the polar or trigonometric form of a complex number
where polar coordinates are r,
called the absolute value or modulus, and j,
that is called the argument, written j
= arg(z). |
| By using
Euler's formula eij
= cosj
+
isinj,
a complex number can also be
written as |
| |
z
= r
eij |
which
is called the exponential form. |
|
|
| To show
the equivalence between the algebraic and the trigonometric form of a complex number, |
| z
= r
eij
= r
(cosj
+
isinj) |
| express
the sine and the cosine functions in terms of the tangent |
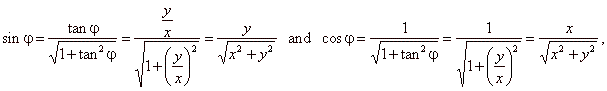 |
| and substitute
into above expression |
|
|
|
| Example: Given
the complex number z
= 1
-
÷3i,
express z
= x
+
yi
in the trigonometric form.
|
| Solution:
The modulus |
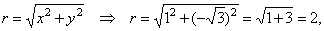 |
|
|
the argument |
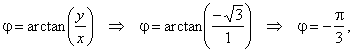 |
|
|
|
|
|
the trigonometric form is
|
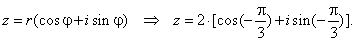 |
|
|
|
| Eulerís formula,
relationship between trigonometric functions and the complex exponential
function |
| Euler's
formula |
| eij
= cosj
+
isinj,
where |
| e
is the base of the natural logarithm,
|
| i is
the imaginary unit, and |
| j is
the angle between x-axis
and the vector pointing to the complex number z
measured counter clockwise, that is, j
is the argument of z, |
|
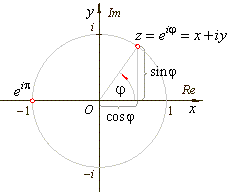
describes the unit circle in the complex plane. |
|
 |
|
| That is,
on the unit circle lie points of the complex plane that correspond to the
complex numbers each of which is one unit far from the origin. |
| Thus, by
plugging the angles, |
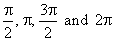 |
into Euler's
formula respectively |
|
|
 |
| obtained
are the four complex numbers that lie on the unit circle, the
two of which lie on the real axis and the two on the imaginary
axis as shows the above picture. |
|
The expression eip
+ 1 = 0 is called Euler's
equation or identity.
|
|
|
Euler's formula shows relations
between trigonometric functions and complex
exponentials. |
|
Thus, by adding and subtracting
Euler's formulas:
|
|
(1) eij
= cosj
+
isinj |
| and
(2) e-ij
= cos(-j)
+
isin(-j)
= cosj
-
isinj |
| and solving for
cosine and sine |
| |
| |
|
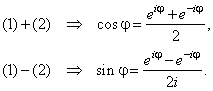 |
|
|
| We use
Euler's formula to write complex number z
= x
+
yi
in polar coordinates, |
| |
z
= x
+
yi = r
(cosj
+
isinj)
= r
eij |
|
|
| where |
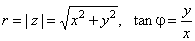 |
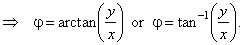 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Intermediate
algebra contents |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved.
|