|
|
|
|
Imaginary
and Complex Numbers |
 Addition and
subtraction of complex numbers
Addition and
subtraction of complex numbers |
 Multiplication and
division of
complex numbers
Multiplication and
division of
complex numbers |
 Polar or trigonometric
notation of complex numbers
Polar or trigonometric
notation of complex numbers |
|
Multiplication
and division of complex numbers in the polar form |
|
Exponentiation
and root extraction of complex numbers examples |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Addition and
subtraction of complex numbers |
| To add or
subtract two complex numbers z1
= a + bi
and z2
= c + di, we add or subtract the real parts
and the imaginary parts. |
| Addition: |
z1 +
z2
= (a + bi) + (c + di) = (a
+ c) + (b + d)i |
|
|
| Subtraction: |
z1
-
z2
= (a + bi) -
(c + di) = (a -
c) + (b -
d)i |
|
|
|
| Examples: Given
are complex numbers, z1
= -3 +
2i and
z2
= 4 + 3i,
find z1 +
z2 and
z1
-
z2.
|
|
Solutions:
z1 +
z2
= (-3 +
2i) + (4 + 3i) =
(-3 +
4) + (2 + 3)i = 1 + 5i
|
|
and
z1
-
z2
= (4 + 3i) -
(1 + 5i) =
(4 -
1) + (3 -
5)i =
3 -
2i |
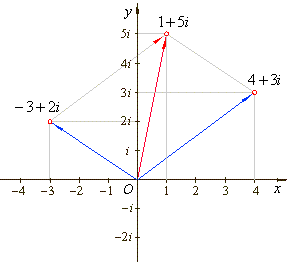
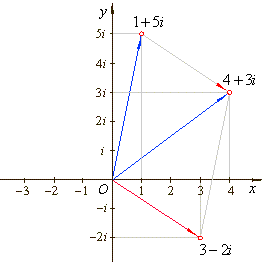
| Given
addition and subtraction are shown in the complex plane in
the figures below. |
| z1 +
z2
=
(-3 +
2i) + (4 + 3i) = 1 + 5i |
|
z1
-
z2
=
(4 + 3i) -
(1 + 5i) = 3 -
2i |
 |
|
 |
|
|
| Multiplication and
division of
complex numbers |
| Multiplication: |
z1∑
z2
=
(a + bi) ∑ (c + di) = ac
+ bci + adi + bdi2
= (ac -
bd) +
(ad + bc)i |
|
|
| Division: |
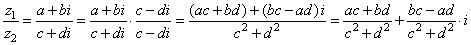 |
|
|
|
| Examples: Given
are complex numbers, z1
= -3 +
2i
and z2
= 4 + 3i,
find z1 ∑
z2
and
z1
/
z2.
|
|
Solutions:
z1 ∑
z2
= (-3 +
2i) ∑ (4 + 3i) =
-3 ∑
4 + 2 ∑ 4i +
(-3)
∑ 3i +
2 ∑ 3 i2
= -18
-
i
|
|
and |
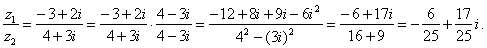 |
|
|
|
|
| Example:
For what real
number
a the real part of the complex number |
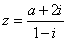 |
equals
1. |
|
|
|
Solution:
|
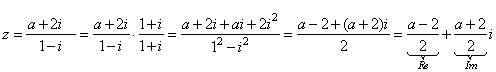 |
| |
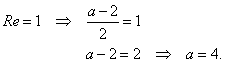 |
|
|
| Example:
Evaluate the
expression |
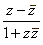 |
where
z = 1 -
i. |
|
|
|
Solution:
|
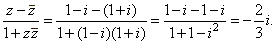 |
|
|
| Polar or trigonometric
notation of complex numbers |
| A point (x,
y)
of the complex plane that represents the complex number z
can also be specified by its distance r
from the origin and the angle j
between the line joining the point to the origin and the
positive x-axis. |
| Cartesian
coordinates expressed by polar coordinates: |
| x
= r cosj |
| y
= r sinj |
| plugged
into z
= x
+
yi
give |
|
z
= r
(cosj
+
isinj), |
|
| where |
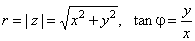 |
|
|
|
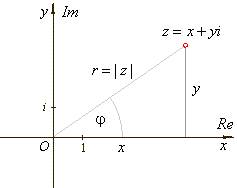 |
|
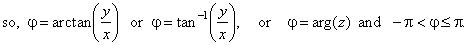 |
| Thus,
obtained is the polar or trigonometric form of a complex number
where polar coordinates are r,
called the absolute value or modulus, and j,
that is called the argument, written j
= arg(z). |
| By using
Euler's formula eij
= cosj
+
isinj,
a complex number can also be
written as |
| |
z
= r
eij |
which
is called the exponential form. |
|
|
| To show
the equivalence between the algebraic and the trigonometric form of a complex number, |
| z
= r
eij
= r
(cosj
+
isinj) |
| express
the sine and the cosine functions in terms of the tangent |
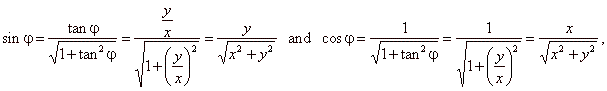 |
| and substitute
into above expression |
|
|
|
| Example: Given
the complex number z
= 1
-
÷3i,
express z
= x
+
yi
in the trigonometric form.
|
| Solution:
The modulus |
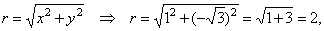 |
|
|
the argument |
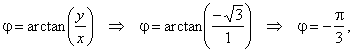 |
|
|
|
|
|
the trigonometric form is
|
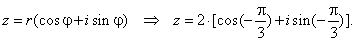 |
|
|
|
| Multiplication
and division of complex numbers in the polar form |
| If
given z1
= r1(cosj1
+ isinj1)
and z2
= r2(cosj2
+ isinj2)
then |
| |
z1
∑ z2 = r1
r2 ∑ [cos(j1
+ j2)
+ isin(j1
+ j2)] |
|
|
| and |
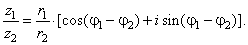 |
|
|
|
|
Exponentiation
and root extraction of complex numbers examples
|
| Example: |
Compute |
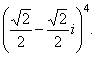 |
|
|
| Solution: |
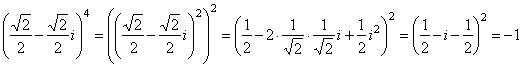 |
|
| or
in the polar form, |
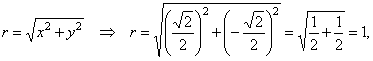 |
|
| and |
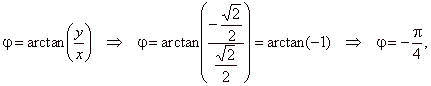 |
|
| since
exponentiation with integer exponent |
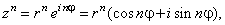 |
|
| then |
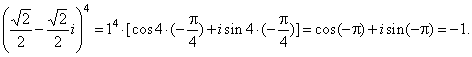 |
|
|
| Example: |
Compute |
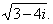 |
|
|
| Solution:
As square root of a
complex number is a complex number, then |
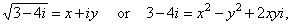 |
| and, two
complex numbers are equal if their real parts are equal and
their imaginary parts are equal, that is |
 |
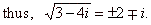 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Intermediate
algebra contents |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved.
|