|
| Geometry - solid figures
solved problems |
|
|
|
 Solid figures, solved problems examples
Solid figures, solved problems examples |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Example:
Height of a cone is 12 and the volume
324p. Find the central angle of the sector to which is unrolled the side
surface of the cone. |
| Solution: Given
h
= 12 and
V = 324p.
a
= ? |
|
|
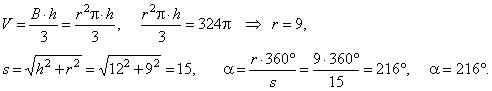 |
| Example:
An isosceles trapezoid
with bases lengths, 3n
and n,
whose base angle is
45°, rotates around
greater base.
Find the volume of the solid of revolution. |
| Solution: Given
bases lengths,
3n
and n,
and base angle 45°.
Vsolid
of revolution = ? |
|
|
| Example:
By rotating the rhomb around its longer diagonal generated is solid whose volume is two times smaller than the
volume of the solid generated by rotating the rhomb around its shorter diagonal. The ratio of diagonals
d1
: d2, (d1
> d2 ),
is? |
| Solution: Given
V1
: V2
= 1
: 2. d1
: d2
= ? |
|
|
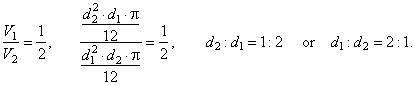 |
| Example:
In a sphere of radius
2
cm inscribed is a cone of the height
3
cm. The ratio of volumes of the cone
and the sphere is? |
| Solution: Given
R
= 2 cm
and h
= 3 cm.
Vconic
: Vsphere
= ? |
|
|
| Example:
The slant height of a cone is
3 cm
and is inclined to the base of the cone at the angle 60°. The surface of the
sphere inscribed in the cone is? |
| Solution: Given
s
= 3 cm and
a
= 60°. S
sphere
= ? The cross section through the apex and center of the
base of the cone is the equilateral triangle. |
|
|
| Example:
A channel’s cross section has the form of the isosceles trapezoid of bottom side
2
m and upper parallel side
4
m and altitude
1
m. How much water is in the channel if it is fulfilled to the half of its height? |
| Solution: Given,
c
= 4 m,
a
= 2 m,
h
= 1 m,
and l
= 100 m.
V
= ? |
|
|
| Example:
An equilateral triangle of the side a =
6 rotates around a line parallel to its side on the distance
that equals the
triangle’s height (not passing through the vertex of the triangle), find the volume of the solid of revolution. |
| Solution: Given a =
6. Vsolid
of revolution = ?
Vsolid
of revolution =
2Vfrustum
-
Vcylinder |
 |
|
|
| Example:
The cosine of the angle at which diagonals of a cube intersect is? |
| Solution: Given
a cube.
cos j
= ? |
|
|
| Example:
In a right triangular prism inscribed is a sphere which touches all faces of the prism. The ratio of surfaces of the
sphere and the prism is? |
| Solution: Given
a right triangular prism.
Ssphere
: Sprism
= ?
Ssphere
= 4R2p, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Geometry
and use of trigonometry contents - B |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |