|
| Trigonometry |
|
|
|
Trigonometric
Functions and Inverse Trigonometric Functions |
 Trigonometric
functions graphs and relations
Trigonometric
functions graphs and relations |
 The
sine function and the cosine function graphs and relations
The
sine function and the cosine function graphs and relations |
 The
tangent function and the cotangent function graphs and relations
The
tangent function and the cotangent function graphs and relations |
 The
cosecant function
and the
secant function graphs and relations
The
cosecant function
and the
secant function graphs and relations |
|
The
cosecant function y
= csc x |
|
The graph of the cosecant
function |
|
The
secant function
y
= sec x |
|
The graph of the secant
function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Trigonometric
functions and inverse trigonometric functions or
arc-functions |
| Trigonometric
functions graphs and relations |
| Trigonometric
(cyclometric) functions are defined as the ratios of the sides of a right
triangle containing the angle equal to the argument of the
function in radians.
|
| Or
more generally for real arguments, trigonometric
functions are defined in terms of the coordinates of the terminal point Q of
the arc
(or angle) of the unit circle with the initial point at P(1,
0). |
|
|
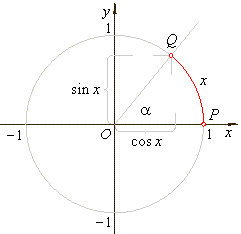 |
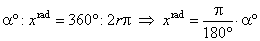 |
| sin2x
+ cos2x
= 1 |
|
|
|
|
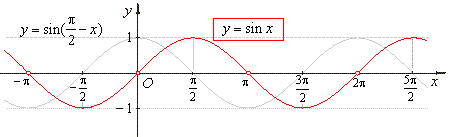
- The
sine function
y
= sin x
is the y-coordinate
of the terminal point of the arc x
of the unit circle. |
|
The
graph of the sine function is the sine curve or sinusoid. |
| In
a right-angled triangle the
sine function is equal to the ratio of the length of the side
opposite the given angle to the length of the hypotenuse. |
 |
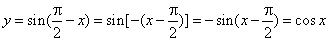 |
|
|
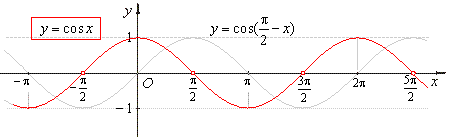
- The
cosine function
y
= cos x
is the x-coordinate
of the terminal point of the arc x
of the unit circle. |
|
The
graph of the cosine function is the cosine curve or cosinusoid. |
| In
a right-angled triangle the cosine function is equal to the
ratio of the length of the side adjacent the given angle to the
length of the hypotenuse. |
 |
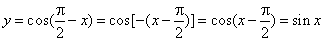 |
|
|
- The
tangent function
y
= tan x
is the ratio of the y-coordinate to
the x-coordinate
of the terminal point of the arc x
of the unit circle, or it is the ratio of the sine function to the cosine function. |
| In
a right-angled triangle the
tangent function is equal to the ratio of the length of the side
opposite the given angle to that of the adjacent side. |
|
|
- The
cotangent function
y
= cot x
is the reciprocal of the tangent function, or it is the ratio of the cosine
function to the
sine function. |
| In
a right-angled triangle the cotangent function is equal to the ratio of the length of the side adjacent
to the given angle to that of the side opposite it. |
|
|
|
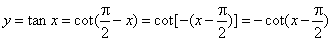 |
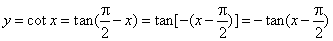 |
|
|
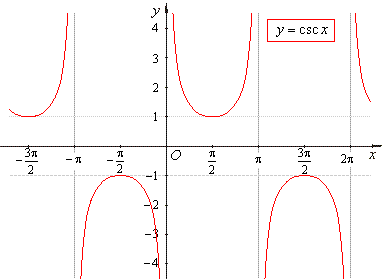
- The
cosecant function
y
= csc x
is the reciprocal of the sine function. |
| In
a right-angled triangle the
cosecant function is equal to the ratio of the length of the
hypotenuse to that of the side opposite to the given angle. |
|
| The
graph of the
cosecant function |
 |
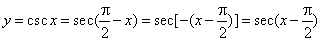 |
|
|
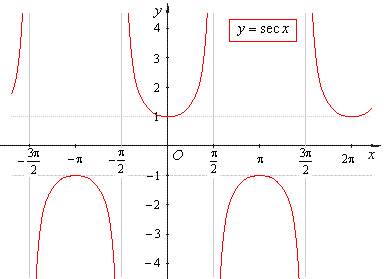
- The
secant function
y
= sec x
is the reciprocal of the cosine function. |
| In
a right-angled triangle the secant function is equal to the
ratio of the length of the hypotenuse to that of the side
adjacent to the given angle. |
|
| The
graph of the
secant function |
 |
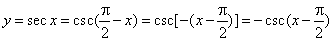 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Functions
contents D |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |