|
| The
graph of Quadratic Function |
|
|
|
|
The
graph of the quadratic function
f
(x)
= x2 |
 Translation of the source quadratic function in the direction of
the y-axis
Translation of the source quadratic function in the direction of
the y-axis |
|
Quadratic
function of the form f
(x)
= x2 + y0 |
 Quadratic
equation
x2
=
a,
a
>
0
Quadratic
equation
x2
=
a,
a
>
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The
graph of the quadratic function
f
(x)
= x2 |
| A function that to every real number associates its square is called
a quadratic function and is denoted |
|
f
(x)
= x2,
x
Î
R.
The point P(x,
x2)
lies on the graph of a quadratic function called a parabola. |
|
|
| For
x
=
0 function
f
(x)
= x2
has minimal value f
(0)
=
02 =
0.
This point is called the turning point or the
vertex
of the parabola.
|
| The
curve is symmetrical about the y-axis and has its vertex
V(0,
0) at the origin. |
| The curve is decreasing for
x < 0 and is increasing for
x
> 0. |
| If
y
=
f
(x),
then y
=
-
f
(x)
is its reflection about the x-axis. |
| Therefore,
the graph of the quadratic f
(x)
= -x2
has its maximum at the vertex. |
| The curve is
increasing for
x < 0 and is decreasing
for x > 0. |
|
| Translation
(or shift) of the source quadratic function in the direction of
the y-axis, quadratic
function of the form f
(x)
= x2 + y0 |
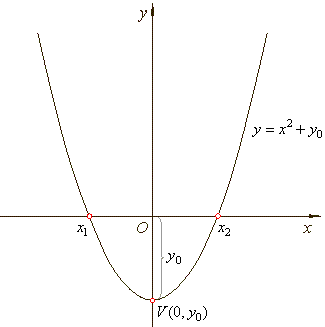
| Translating
the graph of the source quadratic function vertically by y0,
the vertex of the function moves to the point V(0,
y0 ). |
| The
translation or shift is in the positive direction of the y-axis
(upward) if y0
> 0, in the negative direction (downward) if
y0
< 0. |
 |
|
| Points
where a graph crosses or touches the x-axis
are called x-intercepts,
roots or zeros. At the x-intercept
y
= 0. |
| To
find the zeros of the quadratic function, set the function equal
to zero, f
(x)
= 0,
and solve for x. |
| That
is, solve the equation x2 + y0
= 0, |
 |
|
|
|
| Quadratic
equation
x2
=
a,
a
>
0 |
| If
a
> 0 then the quadratic equation
x2
=
a
has two
solutions, |
 |
|
| If a
= 0 then the
equation has zero as the double root, and if a
< 0 then the equation has no real roots. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Beginning
Algebra Contents B |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |