|
|
|
|
Differential
calculus - derivatives
|
|
|
|
Derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions
|
|
1)
The derivative of the inverse of the sine function
y =
sin -1x,
| x | < 1
and -p/2
< y < p/2
if
x = sin y,
then |
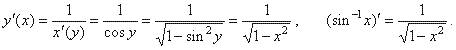 |
| 2)
The derivative of the inverse of the cosine function
y
= cos -1x =
p/2
-
sin
-1x,
| x | < 1,
0
< y < p |
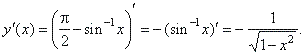 |
|
3)
The derivative of the
inverse of the tangent function y =
tan -1x,
-
oo
< x < oo
and
-p/2
< y < p/2
if
x = tan y,
then |
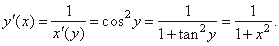 |
| 4)
The derivative of the
inverse of the cotangent function y =
cot -1x
= p/2
-
tan -1x, |
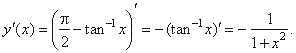 |
| 5)
The derivative of the
inverse of the secant function y =
sec -1x
= cos -1(1/x), |
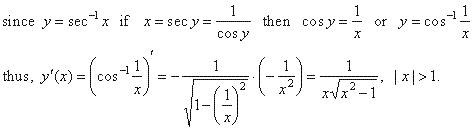 |
| 6)
The derivative of the
inverse of the cosecant function y =
csc -1x
= sin -1(1/x), |
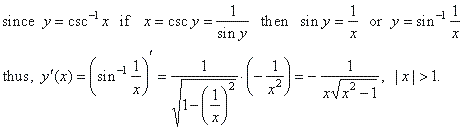 |
|
Therefore,
derivatives of the inverse trigonometric functions are |
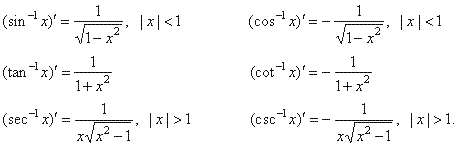 |
|
|
Derivative of
parametric functions, parametric derivatives
|
|
When
Cartesian coordinates of a curve is represented as
functions of the same variable (usually written t),
they are
called the parametric equations. |
| Thus,
parametric equations in the xy-plane |
| x
= x(t)
and y
= y(t)
or x
= f (t)
and y
= g (t), |
| denote
the x
and y
coordinate of the graph of a curve in the plane. |
|
Assume
that f
and g
are differentiable and f
'(t) is not
0 then, given parametric curve can be
expressed as y
= y(x) and this
function is differentiable at x,
that is |
| x
= f (t)
or t = f -1(x),
by plugging
into y
= g(t)
obtained is y
= g [f -1(x)]. |
| Therefore,
we use the chain rule and the derivative of the inverse function to find
the derivative of the parametric
functions, |
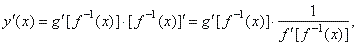 |
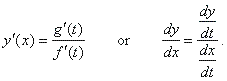 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents
J
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved.
|
|
|