|
The chain rule
applications
|
|
Implicit
differentiation
|
|
Let
given a function F
= [ y (x)] n,
to
differentiate F
we use the power rule and the chain rule,
|
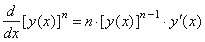 |
| which,
for example, for n =
2 gives |
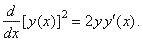 |
|
|
The
same method we use to differentiate an equation of a curve given in the
implicit form
|
| F
(x,
y) = c or
F
(x,
y) = 0. |
|
So,
the chain rule applied to differentiate the above equation with respect
to x
gives
|
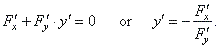 |
|
Meaning,
differentiate the equation with respect to both variables at the same
time such that, when differentiating
with respect to x,
consider y
constant,
while when differentiating
with respect to y,
consider x constant
and multiply by y'. |
|
|
Implicit differentiation examples
|
| Example:
Calculate
the derivative y' of the
equation of the curve x2
+ y2 -
2axy
= 0.
|
|
Solution:
We
use the above method of implicit differentiation to find y'
of the
equation,
|
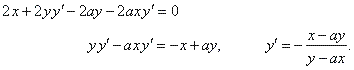 |
|
|
Example:
Let
determine the equation of the line tangent to the ellipse b2x2
+ a2y2 = a2b2
with the center at the origin, at the point (x1,
y1).
|
| Solution:
Differentiating
the equation of the ellipse we get,
|
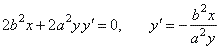
|
|
so
the slope |
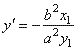 |
of the line
tangent to the ellipse at the point (x1,
y1). |
|
|
Therefore,
the equation of the line tangent to the ellipse
at the point (x1,
y1)
is
|
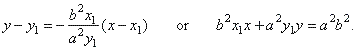 |
|
|
Generalized
power rule
|
|
|
| Example:
Find
the derivative of the function |
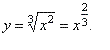 |
|
| Solution:
|
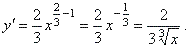 |
|
|
| Example:
Find
the derivative of the function |
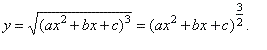 |
|
| Solution:
|
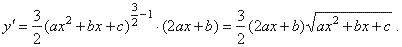 |
|
|
|
Logarithmic differentiation
|
|
The derivative of the logarithm of
a function y
= f (x)
is called logarithmic derivative of the
function, thus
|
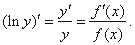 |
|
Therefore, the logarithmic derivative
is the derivative of the logarithm of a given function.
|
|
|
Logarithmic differentiation examples
|
|
Example:
Find
the derivative of the function f(x)
= ln (sin x).
|
| Solution:
|
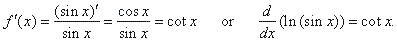 |
|
|
|
|