|
Differentiation
rules
|
|
The
derivative of the sum or difference of two functions
|
|
The
derivative of the sum or difference of two differentiable functions
equals the sum
or difference of their derivatives,
written |
 |
|
|
The
product rule
|
|
The
derivative of the product of two differentiable functions is
equal to, the first function times the derivative of the second
plus the second function times the derivative of the first, |
 |
|
|
A
constant times a function rule
|
|
The
derivative of a constant times a function is equal the constant
times the derivative of the function, where
the
constant c
can be any real number or expression that does not contain the
variable, |
 |
|
|
Derivatives of
functions examples
|
| Example:
Find
the derivative of the function f(x)
= m x
+ c |
| Solution: |
 |
|
|
| Example:
Find
the derivative of the function |
 |
|
| Solution: |
 |
|
|
| Example:
Find
the derivative of the function |
 |
|
| Solution: |
 |
|
|
| Example:
Find
the derivative of the function |
 |
|
| Solution: |
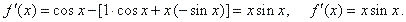 |
|
|
|
The
quotient rule
|
| The
derivative of the quotient of two differentiable functions is,
the denominator times the derivative of the numerator
minus the numerator times the derivative of the denominator all
divided by the denominator squared,
written |
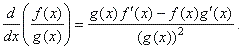 |
| The
quotient rule used to differentiate an expression where a
constant is divided by a function, |
 |
|
|
The
derivative of the tangent function, use of the quotient rule
|
| Since |
 |
then,
we obtain the derivative of the tangent function by using
the quotient rule, so |
|
 |
| Therefore,
if f
(x)
= tan x then |
 |
|
|
|
The
derivative of the cotangent function, use of the quotient rule
|
| Since |
 |
then,
we obtain the derivative of the cotangent function by using
the quotient rule, |
|
 |
| Therefore,
if f
(x)
= cot x then |
 |
|
|
|
The
chain rule
|
| If
y = f
(u)
and u
= g
(x) such that f
is differentiable at u
= g
(x) and g
is differentiable at x,
that is |
 |
|
then,
the composition of f
with g,
y
= (
f o g
)(x)
= f [g
(x)] |
|
is differentiable at x,
and then |
 |
| Thus,
the derivative of a composition of functions is equal to the
derivative of outside function, with respect to the
inside function (i.e., taking it as the independent variable),
times the derivative of the inside function.
|
|
|
Differentiation
using the chain rule examples
|
| Example:
Find
the derivative of the function y =
(x2 -
3x + 5)3. |
| Solution:
Consider
y = f
[g
(x)]
where, y = f
(u) =
u3
and u
= g(x) =
x2 -
3x + 5 |
|
so
that,
|
 |
|
|
Therefore,
|
 |
|
|
| Example:
Find
the derivative of the function y =
sin3 2x = (sin 2x)3. |
| Solution:
Consider
y = f
{g [h
(x)]}
where, y = f
(u) =
u3,
u
= g(v) = sin v
and v
= h(x) = 2x. |
|
so
that,
|
 |
|
|
Therefore,
|
 |
|
|