|
Sum to product and
product to sum formulas or identities
|
|
Sum to product formulas
for the sine and the cosine functions
|
| Adding
and subtracting the sum and difference formulas for the sine function,
|
| sin (a
+ b)
= sin a
· cos b
+ cosa
· sin b
(1) |
| sin (a
-
b)
= sin a
· cos b
-
cosa
· sin b
(2) |
| give,
sin (a
+ b)
+
sin (a
-
b)
= 2sin a
· cos b
and sin (a
+ b)
-
sin (a
-
b)
= 2cosa
· sin b. |
| Then,
substitute, a
+ b
= x and a
-
b
= y
so that, |
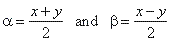 |
|
| thus, |
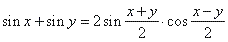 |
and |
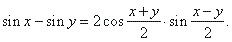 |
|
|
| Adding
and subtracting sum and difference formulas for the cosine function, |
| cos
(a
+ b)
= cos a
· cos b
-
sin a
· sin b
(1) |
| cos
(a
-
b)
= cos a
· cos b
+ sin a
· sin b
(2) |
| give,
cos
(a
+ b)
+ cos
(a
-
b)
= 2cos a
· cos b
and cos
(a
+ b)
-
cos
(a
-
b)
= -2sin
a
· sin b |
|
substitute, a
+ b
= x and a
-
b
= y
so that, |
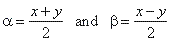 |
|
| thus, |
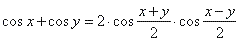 |
and |
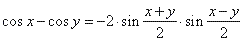 |
|
|
|
|
Sum to product formulas
for the tangent and the cotangent functions
|
| From the definition of the function tangent, |
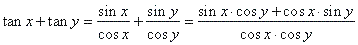 |
| or |
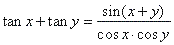 |
and |
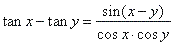 |
|
|
| and
for the function cotangent |
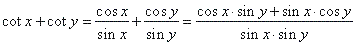 |
|
| or |
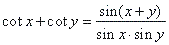 |
and |
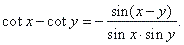 |
|
|
| Using
the same method, |
|
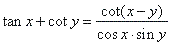 |
and |
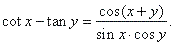 |
|
|
|
|
The product to sum
formulas for the sine and cosine functions
|
| By adding and subtracting addition formulas derived are following product
to sum formulas, |
|
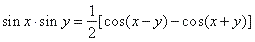 |
and |
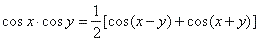 |
|
|
|
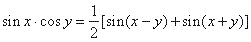 |
and |
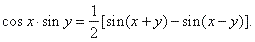 |
|
|
|
|
Trigonometric
identities
examples
|
|
Example:
Use, tan
45°
= 1 and tan
60°
= Ö3,
to prove that tan
15°
= 2 -
Ö3.
|
|
|
| Example:
Prove the identity |
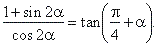 |
|
|
|
| Example:
Prove the identity |
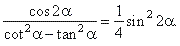 |
|
|
|
|
| Example:
Prove the identity |
|
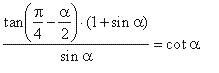 |
|
|
Solution: Substitute |
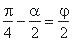 |
|
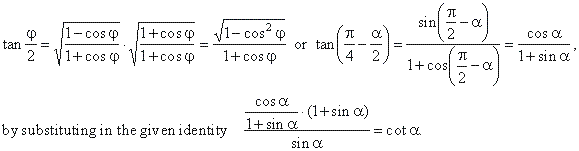 |
|
| Example:
Prove the identity |
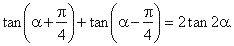 |
|
|
Solution: Using the formula for the sum of the tangent |
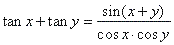 |
|
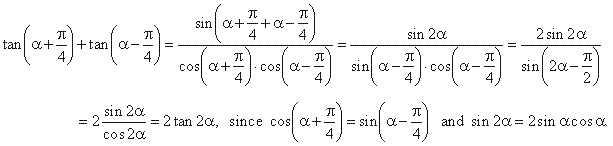 |
|
| Example:
Verify the identity |
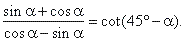 |
|
| Solution:
We divide the numerator and
denominator on the left side by sin
a
and to the right side we use the cotangent formula for the
difference of two angles, thus
|
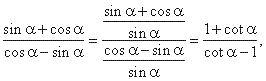 |
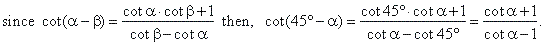 |
|
|
Example:
Express tan
3x in terms of tan
x.
|
| Solution:
Using the sum formula and the double angle formula for the
tangent function, |
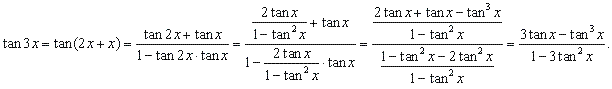 |
|