|
|
|
|
Geometry and use
of trigonometry
|
|
|
|
Circle
|
|
A circle is a set of points that are at the fixed distance (called the
radius r) from a fixed point called the center
O.
|
|
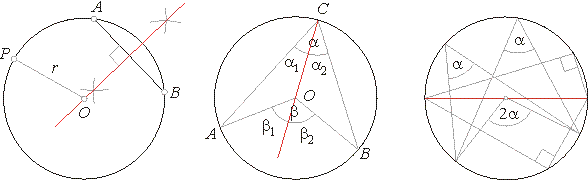
Central angle, inscribed angle
|
|
A
central angle is
double the inscribed angle (formed when two secant lines intersect
on the circle) subtended by the same arc.
|
|
Proof:
Angles
b1
and b2 are
external angles of the isosceles triangle's AOC and
BOC, hence
|
| b1
= 2a1,
b2
= 2a2,
a
= a1+
a2
=> b = b1+
b2
= 2(a1+
a2)
= 2a |
 |
|
Inscribed angles
subtended by the same arc are equal. An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle.
|
|
|
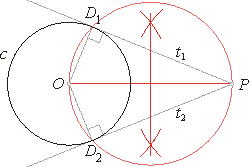
Construction of a tangent
from a point
|
 |
|
Construction of a tangent
from a point P
to a circle c.
|
|
The
midpoint of the line segment OP
is the circumcenter of the quadrilateral PD1OD2.
The lines PD1
and PD2
are tangents from P
to the given circle c.
|
|
Circumference, the length of a circle - the perimeter
|
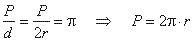 |
|
|
|
Length of an arc
|
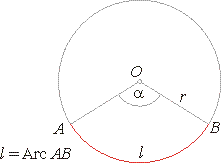 |
| Applying
the proportion, |
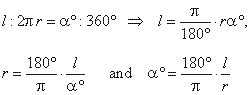 |
|
|
|
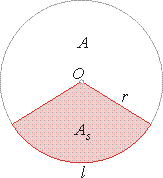
Circle and circular sector
|
|
By substituting
P = 2pr
and R
= r
in the formula for the area of a regular polygon, obtained is the formula
for the area of a circle, that is
|
 |
|
|
|
|
| substituting
|
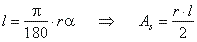 |
|
|
|
|
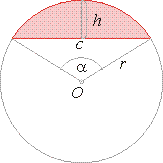
Circular segment
|
|
The portion of a circle bounded by an arc and a chord is called a segment.
Symbols
used in the formulas: c
-chord, r
-radius, h
-height of a segment, A
-area of a segment.
|
 |
|
|
|
Annulus and annulus segment
|
| Annulus
or ring is the region enclosed between two concentric circles. |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid
geometry
|
|
Prism
|
| A
prism is a polyhedron (having five or more faces) with two parallel and congruent polygonal bases, so
that all cross-sections taken parallel to the bases are also congruent with the
bases, thus all lateral faces (sides) are parallelograms.
Lateral
faces meet in line segments called lateral
edges. |
| A
right prism is one whose lateral
faces and lateral edges are perpendicular to its bases. The
lateral faces of a right prism are all rectangles, and the
height of a right prism is equal to the length of its lateral
edge. |
| A
regular prism has regular polygons as bases. A regular
polygon is one that has all sides equal in length and all angles
equal in measure. |
| Thus,
a right regular prism is one with
regular polygon bases and perpendicular rectangular lateral
sides. |
| Meaning
of symbols used in pictures and in
formulas are, |
| d
- diagonal, h
- altitude, P
- perimeter of base,
B
- base,
S
- surface
of a solid figure, Slat
-
lateral surface, V
-
volume of a solid figure. |
|
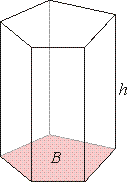 |
| S
= 2B + Slat
-
surface of a prism |
|
Slat = P ·
h
-
lateral surface |
| V
= B · h
- volume
of a prism |
| B
- area of
base, P
- perimeter of base, h
- height
of a prism |
|
|
|
|
Cube
|
|
|
|
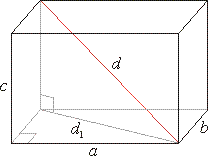
Rectangular prism or
rectangular parallelepiped (cuboid)
|
|
A
solid of which the six faces are mutually perpendicular
rectangles is called a rectangular parallelepiped or
a rectangular prism.
|
 |
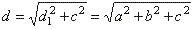 |
| S
= 2B + Slat
= 2(ab + ac + bc)
-
surface |
| V
= B · h = a
· b · c
- volume |
|
|
|
|
Right triangular prism
|
|
A
right triangular prism is made of two triangular bases and three
rectangular faces with lateral edges perpendicular to the bases. |
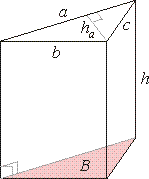 |
| S
= 2B + Slat
= a
ha + (a + b + c)· h
-
surface |
| V
= B · h = 1/2 ·
a
ha · h
- volume |
|
|
|
|
Regular right triangular prism
|
|
|
|
Regular right hexagonal prism
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contents
D
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved.
|
|
|