|
| Trigonometry |
|
|
|
|
 Trigonometric
functions of double angles, double angle formulas
Trigonometric
functions of double angles, double angle formulas |
|
Trigonometric functions expressed by the half
angle |
|
Trigonometric
functions of double angles expressed by the tangent function |
 Trigonometric functions expressed by the
cosine of the double angle
Trigonometric functions expressed by the
cosine of the double angle |
 Trigonometric identities,
examples
Trigonometric identities,
examples |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Trigonometric
functions of double angles, double angle formulas |
|
By substituting b
with
a
in the sum formulas, |
|
sin (a
+ b)
= sin a
· cos b
+ cosa
· sin b
and cos
(a
+ b)
= cos a
· cos b
-
sin a
· sin b, |
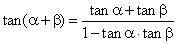 |
and |
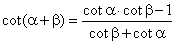 |
|
| thus
for example, sin
2a
= sin (a
+ a)
= sin a
· cos a
+ cosa
· sin a
= 2sin a
cos a
so we get, |
| |
sin
2a
= 2 sin a
cos a |
and |
cos
2a
= cos2 a -
sin2 a |
|
|
|
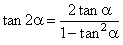 |
and |
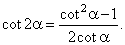 |
|
|
|
|
The double angle formula for the cosine function can be expressed
by sine or cosine function using the identity sin2 a
+ cos2 a
= 1, |
| |
cos
2a
=
2cos2 a -
1 |
or |
cos
2a
= 1
-
2sin2 a |
|
|
|
and |
1
+ cos
2a
=
2 cos2 a |
or |
1
-
cos
2a
=
2sin2 a |
|
|
|
|
|
Trigonometric functions expressed by the
cosine of the double angle
|
|
Replacing a/2
by a
in the above identities, we get
|
|
|
|
| Trigonometric identities,
examples |
| Example:
Express sin
3x in terms of sin
x. |
| Solution:
Using the sum formula and the double angle formula for the sine function, |
| sin
3x
= sin (2x + x)
= sin 2x · cos x + cos 2x · sin x
= 2sin x cos x · cos x + (cos2 x
-
sin2 x) · sin x |
|
= 2sin x · (1 -
sin2 x) + (1 -
2sin2 x) · sin x = 3sin x -
4sin3 x. |
|
| Example:
Express tan
3x in terms of tan
x. |
| Solution:
Using the sum formula and the double angle formula for the
tangent function, |
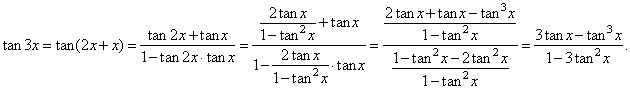 |
|
| Example:
Prove the identity |
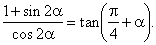 |
|
|
|
|
| Example:
Prove the identity |
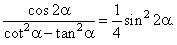 |
|
|
|
|
| Example:
Prove the identity |
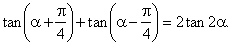 |
|
| Solution:
Using the formula for the sum of the tangent |
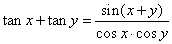 |
|
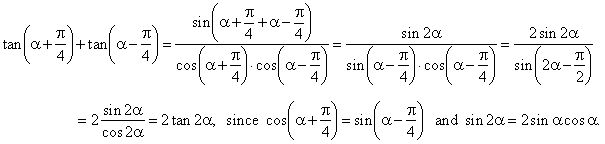 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Pre-calculus contents
F |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |