|
| Coordinate
Geometry (Analytic Geometry) in Three-dimensional Space |
|
|
Plane
in a three-dimensional (3D) coordinate system |
 Equations of
a plane in a coordinate space
Equations of
a plane in a coordinate space
|
 The equation of a
plane in a 3D coordinate system
The equation of a
plane in a 3D coordinate system |
 The Hessian normal form of the
equation of a plane
The Hessian normal form of the
equation of a plane
|
 The intercept
form of the equation of a plane
The intercept
form of the equation of a plane |
 A plane in a 3D
coordinate system, examples
A plane in a 3D
coordinate system, examples |
|
Equation of the
plane through three points example |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Equations of a plane in a coordinate space
|
| The equation of a
plane in
a
3D coordinate system |
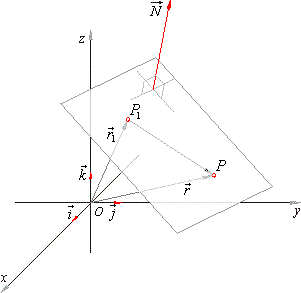
| A plane in space is defined by three points (which don’t all lie on the same line) or by a point and a normal
vector to the plane. |
| Then, the scalar product of the vector
P1P
= r -
r1, drawn from the
given point P1(x1,
y1, z1) of the plane to any point
P(x,
y, z)
of the plane, and the normal vector N
= Ai + Bj
+ Ck, is zero, that is |
| |
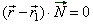 |
which is called the vector equation of a
plane. |
|
|
Or,
|
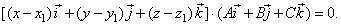 |
|
|
| Therefore, |
| (x
-
x1)
· A
+ (y -
y1)
· B
+ (z -
z1)
· C
= 0 |
| giving |
A
· x
+ B · y
+ C · z
+ D = 0 |
|
|
|
where, D
=
-
(Ax1+
By1+
Cz1) |
|
the general equation of a plane in 3D
space. |
| If plane passes through the origin
O
of a coordinate system then its coordinates, x =
0, y
= 0, and z
= 0 plugged into the equation of the plane, give |
| A
· 0
+ B · 0
+ C · 0
+ D = 0 => D = 0. |
| Thus, the condition that plane passes through the |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| The Hessian normal form of the
equation of a plane
|
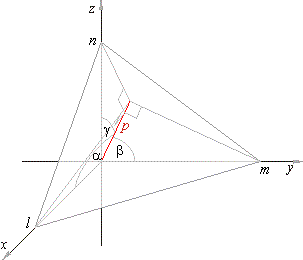
| Position of a plane in space can also be defined by the length of the normal, drawn from the origin to the plane
and by angles,
a, b and
g, that the normal forms with the
coordinate axes.
|
| If
N°
is the unit vector of the normal then its components are, cosa,
cosb
and
cosg.
|
| Then the projection of the position vector
r, of any point
P(x,
y, z) of the plane, onto the normal has the length
p. |
| Since the projection is determined by expression |
 |
| that is,
r
· N°
= p or
written in the coordinates |
| |
x
· cosa
+ y · cosb
+ z · cosg
-
p = 0 |
|
|
| represents the
equation of a plane in the Hessian
normal
form. |
|
 |
|
|
| The intercept form of the equation of a
plane
|
| If,
l,
m
and n
are the intercepts of
x,
y
and z
axes and a plane respectively, then projections of these segments in
direction of the normal drawn from the origin to the
plane are all equal to the length of the normal, that is
|
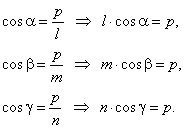 |
| By plugging these values of cosines into Hessian normal
form of the equation of plane, obtained is
|
|
|
| the intercept form of the equation of plane. |
|
 |
|
|
| A
plane in
a
3D coordinate system
examples |
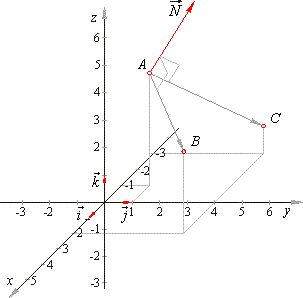
| Example:
Find the equation of
the plane through three points, A(-1,
1, 4), B(2,
4, 3)
and C(-3,
4, 1).
|
| Solution: |
| Equation of a plane
Ax
+ By
+ Cz
+ D = 0 is determined by
the components (the
direction cosines)
of the normal vector N
= Ai + Bj
+ Ck and
the coordinates of any point of the plane. |
| The normal vector is perpendicular to the plane determined by given
points, and as the vector |
| AB
= rB -
rA
= (2i + 4j + 3k)
-
(-i
+ j + 4k)
|
|
rB
-
rA
= 3i + 3j -
k,
and the vector
|
|
AC =
rC -
rA
= -2i
+ 3j -
3k
|
| then,
|
|
 |
|
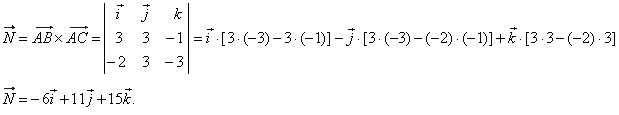 |
| By plugging the coordinates, of any given point, into equation
of the plane determines the value of the coefficient
D.
Thus, plugging |
| A(-1,
1, 4) into
-
6x
+ 11y + 15z + D = 0
gives -
6
· (-1)
+ 11
· 1
+ 15
· 1
+ D = 0, D = -77. |
| Therefore,
-
6x + 11y + 15z -
77 = 0 is the equation of the plane
the given points lie on. |
| The coordinate of the remaining two points
B
and C
must also satisfy the obtained equation, prove. |
|
| Example:
Given are points,
A(-1,
1, 1)
and B(3,
-2,
6), find the equation of a plane which is normal to
the
vector
AB
and passes through the point A.
|
| Solution:
According to the given conditions
the vector
AB
= N
so,
|
| N
= rB -
rA
= (3i -
2j + 6k)
-
(-i
+ j + k) = 4i
-
3j + 5k
|
| As the plane should pass through the point
A |
| plug
A(-1,
1, 1) into
4x -
3y + 5z + D = 0
=>
4 · (-1)
-
3 · 1
+ 5
· 1
+ D = 0,
D = 2 |
| Therefore,
the equation of the plane P
::
4x -
3y + 5z + 2 = 0. |
|
|
| Example:
Segments that a plane cuts on the axes,
x
and y, are
l = -1 and
m = -2
respectively, find the standard or general equation of the plane if it passes through the point
A(3, 4, 6).
|
| Solution:
As the given point A(3, 4,
6) and the segments, l =
-1 and
m = -2
must satisfy the intercept form of the equation of plane,
then
|
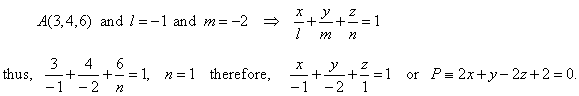 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Pre-calculus contents
J |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |