|
| Trigonometry |
|
|
 Inverse Trigonometric Functions or
Arc-functions and their Graphs
Inverse Trigonometric Functions or
Arc-functions and their Graphs |
 The
arc-tangent function and the
arc-cotangent function
The
arc-tangent function and the
arc-cotangent function |
|
The
arc-tangent function |
|
The
arc-cotangent function |
|
The
graph of the
arc-tangent function and the
arc-cotangent function |
 The
arc-cosecant function and the arc-secant function
The
arc-cosecant function and the arc-secant function |
|
The
graph of the
arc-cosecant and the
arc-secant function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The
arc-tangent function and the
arc-cotangent function |
|
- The
arc-tangent function
y
= tan-1x
or y
= arctan x
is the inverse of the tangent function, so that its
value for any
argument is an arc (angle) whose tangent equals the given
argument. |
| That
is, y
= tan-1x
if and only if x
= tan
y.
For
example, |
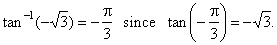 |
|
|
Thus, the arc-tangent
function is defined for all real arguments, and its principal
values are by
convention taken to be those strictly between -p/2
and p/2. |
|
|
- The
arc-cotangent function
y
= cot-1x
or y
= arccot x
is the inverse of the cotangent function, so that
its value for any
argument is an arc (angle) whose cotangent equals the given
argument. |
| That
is, y
= cot-1x
if and only if x
= cot
y.
For
example, |
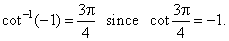 |
|
|
Thus, the arc-cotangent
function is defined for all real arguments, and its principal
values are by
convention taken to be those strictly between 0
and p. |
|
| The
graph of the
arc-tangent function and the
arc-cotangent function |
|
|
|
| The
arc-cosecant function and the arc-secant function |
|
- The
arc-cosecant function
y
= csc-1x
or y
= arccsc x
is the inverse of the cosecant function, so that its
value for any
argument is an arc (angle) whose cosecant equals the given
argument. |
| That
is, y
= csc-1x
if and only if x
= csc
y.
For
example, |
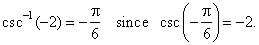 |
|
|
Thus, the arc-cosecant
function is defined for arguments less than -1
or greater than 1, and its principal
values are by
convention taken to be those between -p/2
and p/2. |
|
|
- The
arc-secant function
y
= sec-1x
or y
= arcsec x
is the inverse of the secant function, so that its value for any
argument is an arc (angle) whose secant equals the given
argument. |
| That
is, y
= sec-1x
if and only if x
= sec
y.
For
example, |
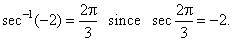 |
|
|
Thus, the arc-secant
function is defined for arguments less than -1
or greater than 1, and its principal
values are by
convention taken to be those between 0
and p. |
|
| The
graph of the
arc-cosecant and the
arc-secant function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Functions
contents D |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |