|
| Conic
Sections |
|
|
|
|
|
Ellipse
|
 Equation of the ellipse, standard
equation of the ellipse
Equation of the ellipse, standard
equation of the ellipse
|
|
Major axis, minor axis, and
vertices
|
|
The focal parameter, latus rectum
|
 The parametric equations of the ellipse
The parametric equations of the ellipse |
|
Ellipse examples |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Equation of the ellipse, standard
equation of the ellipse
|
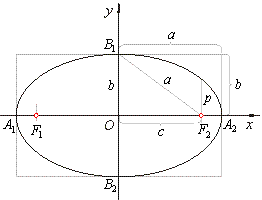
| If in the direction of axes we introduce a coordinate system so that the center of the ellipse coincides with the |
|
origin, then coordinates of foci are |
| F1(-c, 0) and
F2(
c, 0). |
| For every
point P(x,
y) of the ellipse, according to |
| definition
r1 + r2 =
2a, it follows
that |
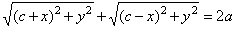 |
| after
squaring |
|
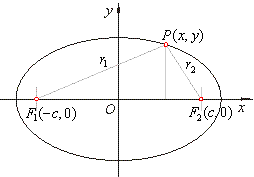 |
|
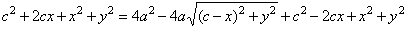 |
| and
reducing |
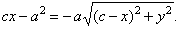 |
|
| Repeated squaring and grouping gives |
| (a2
-
c2) · x2
+ a2y2 = a2
· (a2 -
c2), |
|
|
| follows |
b2x2
+ a2y2 = a2b2 |
equation
of the ellipse, |
|
|
 |
|
| and after division by
a2b2, |
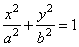 |
standard equation of the ellipse. |
|
|
It follows from the equation that an ellipse is defined by values of
a
and b, or as they are associated through
the relation a2
-
c2 = b2,
we can say that it is defined by any pair of these three quantities. |
| Intersections of an ellipse and the coordinate axes we determine from equation |
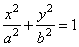 |
by
putting, |
|
| y
= 0 =>
x
= + a,
so obtained are vertices at the ends of the major axis A1(-a,
0) and
A2(a,
0), and |
| x
= 0 =>
y = + b,
obtained are co-vertices, the endpoints of the minor axis B1(0,
b) and
B2(0,
-b). |
The line segments
A1A2
= 2a and
B1B2
= 2b are the
major and
minor axes while
a and b
are the
semi-major and
semi-minor axes respectively. So the arc of the radius
a
centered at B1and
B2 intersects the major axis at
the foci F1and
F2. |
The focal parameter, called latus rectum and denoted
2p, is the chord perpendicular to the major axis
passing through any of the foci, as shows the above figure. The length of which equals the absolute value of ordinates of the points of the ellipse whose abscissas x
= c
or x
= -c
that is |
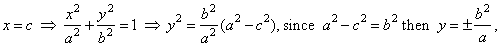 |
| so
the length of the latus rectum |
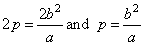 |
the
length of the semi-latus rectum of the ellipse. |
|
|
| The parametric equations of the
ellipse |
| Equation of the ellipse in the explicit form |
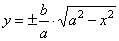 |
can help us to explain another construction |
|
| of
the ellipse. So, in the coordinate system draw two concentric circles of radii equal to lengths of the semi axes a and b, with the center at the origin as shows the figure. |
An arbitrary chosen line through the origin intersects the
circle of the radius a
at the point R
and the circle of radius b
at M.
|
|
Then, the parallel line with the major axis through M
intersects the parallel line with the minor axis through
R, at
a point P(x,
y) of the ellipse.
Proof, |
| in
the figure, OS
= x,
PS
= y
and |
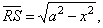 |
|
|
as the triangles
OMN
and ORS
are similar, then
|
|
OM
: OR
= MN
: RS
or b
: a
= PS
: RS,
|
| so
that |
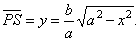 |
|
|
 |
|
| It proves that the point
P(x,
y) obtained by the construction
lies on the ellipse. This way, using the figure, we also derive |
| the
parametric equations of
the ellipse |
 |
where the parameter
t
is an angle 0
<
t
<
2p. |
|
| By dividing the first parametric equation by
a
and the second by b, then square and add them, obtained is
standard equation of the ellipse. |
|
| Ellipse
examples |
| Example:
Given is equation of the ellipse
9x2
+ 25y2 = 225, find the lengths of semi-major and
semi-minor axes, coordinates of the foci, the eccentricity and the length of the
semi-latus rectum. |
| Solution: From the standard equation |
 |
we can find the semi-axes
lengths dividing the given |
|
| equation by
225, |
 |
|
|
coordinates of the
foci F1(-c, 0) and
F2(
c, 0),
since
|
 |
 |
|
| Example:
From given quantities of an ellipse determine remaining unknown quantities and write equation
of the ellipse, |
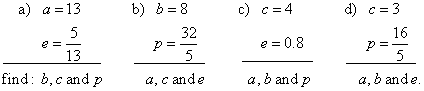 |
| Solution:
a) Using |
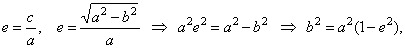 |
|
| therefore,
the semi-minor axis |
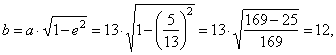 |
|
| the
linear eccentricity |
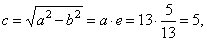 |
|
| the
semi latus rectum |
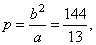 |
and
the equation of the ellipse |
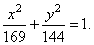 |
|
|
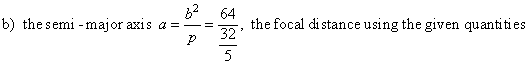 |
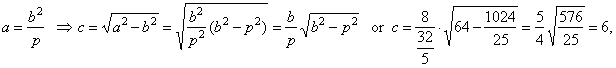 |
| the eccentricity |
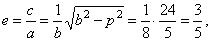 |
and
the equation of the ellipse |
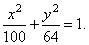 |
|
|
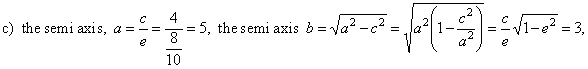 |
| the
semi latus rectum |
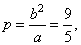 |
and
the equation of the ellipse |
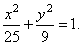 |
|
|
|
d) unknown quantities expressed through given values, |
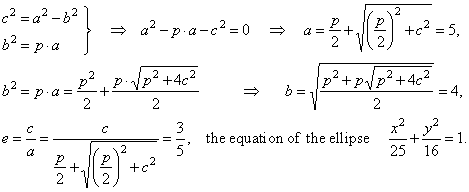 |
|
| Example:
Find the equation of
the ellipse whose focus is F2(6,
0) and which passes through the point
A(5Ö3,
4). |
| Solution:
Coordinates of the point
A(5Ö3,
4) must satisfy equation of the ellipse, therefore |
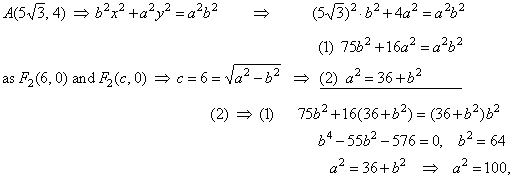 |
|
thus,
the equation of the ellipse |
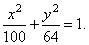 |
|
|
|
| Example:
Write equation of the ellipse passing through points
A(-4,
2) and B(8,
1). |
| Solution:
Given points must satisfy equation of the ellipse, so |
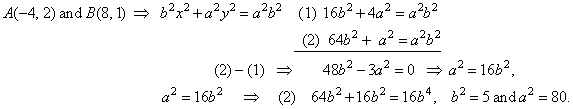 |
| Therefore,
the equation of the ellipse |
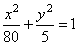 |
or
x2
+ 16y2 = 80. |
|
|
| Example:
In the ellipse 4x2
+ 9y2 = 144 inscribed is a rectangle whose vertices lie on the ellipse and
whose sides are parallel with ellipse axes. Longer side, which is parallel to the major axis, relates to the shorter
side as 3 :
2. Find the area of the rectangle. |
| Solution: It follows from the given condition that the coordinates
of vertices of the rectangle must satisfy the |
|
same ratio, i.e.,
x :
y
= 3 :
2 =>
x =
3y/2.
|
| To determine points of the ellipse of which coordinates are in this ratio, put these variable
coordinates into equation of the ellipse, |
| P(3y/2,
y) =>
4x2
+ 9y2 = 144 |
|
4(3y/2)2
+ 9y2 = 144 =>
18y2 = 144,
|
|
y1,2 = ±Ö144/18 =
±2Ö2,
x =
3y/2 =>
x1,2 =
±3Ö2.
|
|
Therefore, the vertices of the rectangle,
|
|
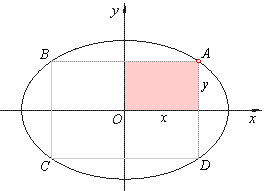 |
|
| A(3Ö2,
2Ö2),
B(-3Ö2,
2Ö2),
C(-3Ö2,
-2Ö2)
and D(3Ö2,
-2Ö2). |
| The
area of the rectangle A =
4 · x
· y =
4 · (3Ö2
)
· (2Ö2
)
=
48 square units. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|