|
|
Vectors in a Plane and Space |
|
 The vector product
and the mixed product use, examples
The vector product
and the mixed product use, examples |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The vector product
and the mixed product use examples |
| Example:
Given are vectors, a
= i -
2 k and
b =
-
i + 3 j + k, determine the vector
c
= a
´
b
and the area of a parallelogram formed by vectors, a
and b.
|
| Solution: |
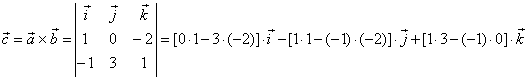 |
|
|
|
| The area of the
parallelogram, |
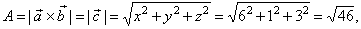 |
| or |
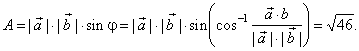 |
|
|
 |
|
|
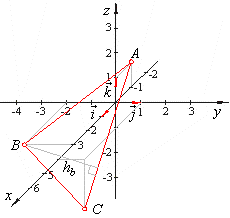
| Example:
Vertices of a triangle are, A(-1,
0, 1), B(3,
-2,
0) and C(4,
1, -2),
find the length of the altitude hb.
|
|
Solution:
Using the area of
a triangle,
|
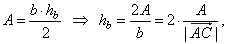 |
| as
the area of the triangle
|
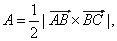 |
where |
|
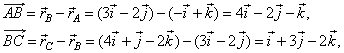 |
|
 |
|
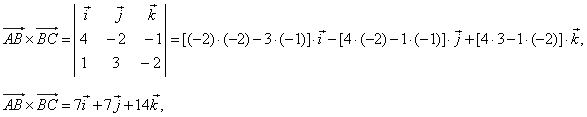 |
| then,
the area of the triangle, |
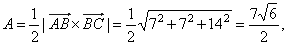 |
|
|
| and the
length of the side b, |
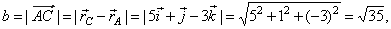 |
|
|
|
| thus,
the length of the altitude, |
|
|
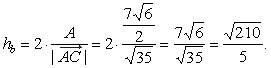 |
|
|
|
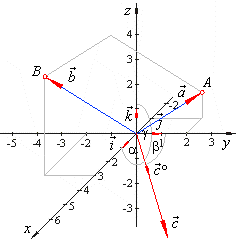
| Example: Find the angles that
the unit vector, which is orthogonal to the plane formed by vectors,
|
| a
= -i +
2 j + k
and b
= 3i -
2
j + 4k,
makes with the coordinate axes. |
|
Solution:
The unit vector which is orthogonal to the plane,
formed by the vectors, a
and b,
is the direction vector of a vector c,
such that
|
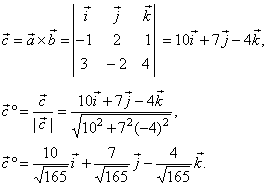 |
|
 |
|
| Angles, which the unit vector
c°
forms with coordinate axes, we find by using the formula, |
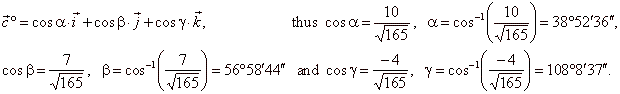 |
|
| Example: Given are vectors,
a
= -2i -
3 j,
b
= -i -
2
j + 3k
and c
= -i +
2
j + k,
find the projection
(the scalar component) of the vector a
onto vector d
= b ´
c.
|
| Solution:
Let first find
the vector d, |
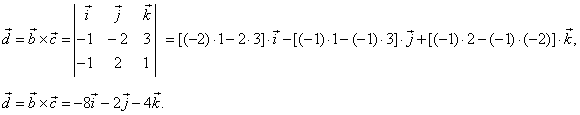 |
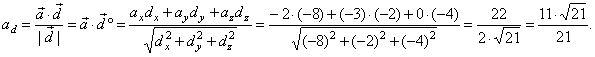 |
|
Example: Given are vectors,
a
= -3i +
4 j -
l
k,
b
=
2i -
j + k
and c
= i
-
4 j -3l
k,
determine the
parameter l
such that vectors to be coplanar. |
Solution:
Vectors lie on the same plane if their scalar triple product is zero, i.e.,
V =
0, therefore vectors’
coordinates must satisfy the condition, |
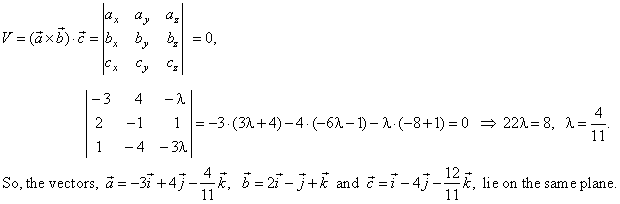 |
|
| Example: Examine if vectors,
a
= 4i + 2 j +
k,
b
= 3i + 3 j -
2k
and c
= -
5i
-
j -
4k,
are coplanar and if so,
prove their linear dependence. |
| Solution:
Check for coplanarity, |
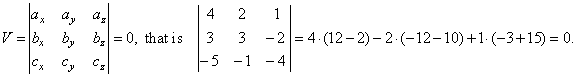 |
| Since vectors are coplanar each of them can be represented as linear combination of other two. |
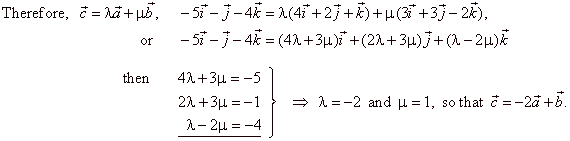 |
|
| Example: Prove that points,
A(-2,
1, 0), B(3,
-2,
-1), C(1,
-1,
2) and D(-3,
2, -5),
all lie on the same plane. |
| Solution:
If all given points belong to the same plane then vectors,
AB,
AC
and AD
are coplanar, therefore the scalar triple product (AB
´
AC)
· AD
= 0. |
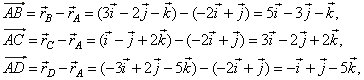 |
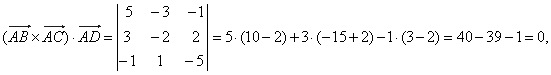 |
| thus, all
given points lie on the same plane. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Pre-calculus contents
I |
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |
|
|