|
| Trigonometry |
|
|
Trigonometric
Equations |
 Trigonometric equations
examples
Trigonometric equations
examples |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Trigonometric equations
examples |
|
Example: Solve the equation,
3
sin
(x
+ 70°) + 5
sin
(x
+ 160°) = 0.
|
|
Solution: Given equation
can be written as
|
| 4
sin
(x
+ 70°) - sin
(x
+ 70°) + 4
sin
(x
+ 160°)
+ sin
(x
+ 160°) = 0 |
|
or
4
[sin
(x
+ 70°)
+ sin
(x
+ 160°)] =
sin
(x
+ 70°) - sin
(x
+ 160°) |
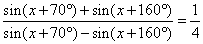 |
| then, by using sum to product formula
|
|
|
|
cot
(- 45°) · tan
(x
+ 115°) = 1/4
or tan
(x
+ 115°) = - 1/4,
|
| therefore,
the solution x
+ 115° = tan-1
, x =
-115°
+ tan-1
(-1/4) =
- 129°2′10″ + k · 180°. |
|
|
Example: Find the solution
of the equation, 2
sin
(x
+ 60°) · cos
x = 1.
|
|
Solution: Applying products as sums formula
|
| 2 · (1/2)
[sin
(x
+ 60°
+ x)
+ sin
(x
+ 60° - x)] = 1
or sin
(2x
+ 60°)
+ sin 60° = 1
|
| then
sin
(2x
+ 60°) = 1
- Ö3/2,
2x
+ 60° =
sin-1(1
- Ö3/2) + k · 360° |
|
and 2x′
+ 60° =
180°
- sin-1(1
- Ö3/2) + k · 360° |
| so,
the solution is 2x =
-
60°
+ sin-1(1
- Ö3/2) + k · 360°,
x =
-
26°9′1″ + k · 180°, |
|
2x′ =
120° - sin-1(1
- Ö3/2) + k · 360°,
x′ = 56°9′1″ + k · 180°,
k Î Z. |
|
|
Example: Find the solution
of the equation, |
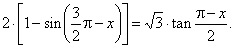 |
|
| Solution: Using
identities |
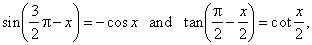 |
|
| given
equation becomes 2 · (1
+ cos x) - Ö3 · cot x/2 = 0, |
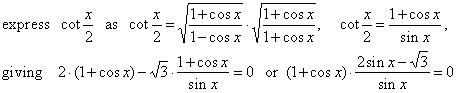 |
| therefore,
1
+ cos x
= 0,
cos
x
= -
1,
x
= p
+ k · 2p, |
|
and 2sin
x -
Ö3
= 0,
sin
x
= Ö3/2,
x
= p/3
+ k · 2p
and x′ = 2p/3
+ k · 2p,
k Î Z. |
|
|
Example: Solve the equation,
cos
2x
+ cos
6x - cos
8x -
1 = 0.
|
|
Solution: To the first two terms apply the sum to product formula and remaining two terms transform using
|
| known identity, thus |
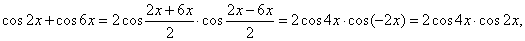 |
| and
since 1
+ cos
2x = 2cos
2 x
then, 1
+ cos
8x = 2cos
2 4x plugging into the
given equation |
| 2cos
4x · cos
2x -
2cos
2 4x
= 0
or 2cos
4x · (cos
2x -
cos
4x)
= 0 |
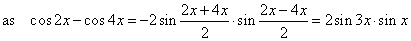 |
| it
follows that 4cos
4x · sin
3x · sin
x
= 0
meaning,
cos
4x
= 0,
sin
3x
= 0
and/or sin
x
= 0.
Since |
| sin
3x
= sin (x
+ 2x)
= sin
x · cos
2x + cos
x · sin
2x
= sin
x · (cos
2 x -
sin
2 x) + cos
x · 2sin
xcos
x |
|
=
sin
x · (1 -
2sin
2 x) + 2sin
x · (1 -
sin
2 x)
=
3sin
x -
4sin
3 x,
|
|
solutions of the equation
sin
x
= 0
are included in the solutions of sin
3x
= 0.
|
|
If sin
x
= 0
then,
sin
3x
= 3sin
x -
4sin
3 x
= sin
x · (3 -
4sin
2 x)
= 0.
|
|
Therefore, the solution set of the given equation is the union of the solutions of each of the equations, that is
|
|
cos
4x
= 0,
4x
=
+ p/2
+ k · 2p,
x
=
+ p/8
+ k · p/2
|
|
and sin
3x
= 0,
3x
= k · p,
x
= k · p/3,
k Î Z.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Pre-calculus contents
G |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |