|
| Trigonometry |
|
|
Trigonometric
Equations |
 The Equations,
tan
(bx
+ c) = m
and
cot
(bx
+ c) = m,
where
b,
c and
m are real
numbers.
The Equations,
tan
(bx
+ c) = m
and
cot
(bx
+ c) = m,
where
b,
c and
m are real
numbers.
|
|
The
Equation
tan
(bx
+ c) = m, example |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The Equations,
tan
(bx
+ c) = m
and
cot
(bx
+ c) = m,
where
b,
c
and m
are real numbers. |
| The given equations can be written as F(bx +
c) = m
where F
substitutes a trigonometric function, x
is an arc
to be calculated and m
is a value of a given trigonometric function. |
| To every trigonometric function we can determine an arc, a +
k · P of which function value equals
m
that is F(a +
k · P) = m,
where a
= x0
is the basic solution, and P
is the period, then |
| F(bx +
c) = F(a +
k · P)
or bx +
c = a +
k · P,
thus |
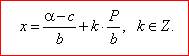 |
| Thus, from obtained general solution we can write a common solutions for every given
equation, |
 |
|
|
| The Equation
tan
(bx
+ c) = m, example |
|
Example: Solve
the equation, |
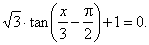 |
|
|
Solution: Rewrite
the equation to the form tan
(bx + c) = m,
|
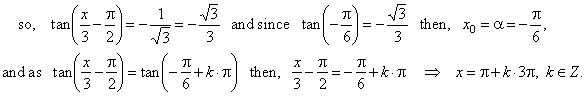 |
| We obtain the same result if we put given parameters,
b,
c, and corresponding basic solution |
| x0
= a
= tan-1
m to the common
solution that is, b
= 1/3,
c = -
p/2 and
x0
= a
= tan-1(-Ö3/3) =
-
p/6 |
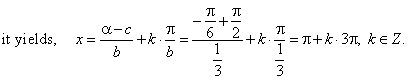 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Pre-calculus contents
G |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |