|
| Quadrilaterals,
Polygons - Regular Polygons, Circle |
|
|
|
Quadrilaterals |
 Square
Square
|
 Rhombus
Rhombus
|
 Rectangle
Rectangle |
 Parallelogram
Parallelogram |
 Kite
or deltoid
Kite
or deltoid
|
 Trapezium
or trapezoid
Trapezium
or trapezoid
|
 Isosceles
trapezoid
Isosceles
trapezoid
|
 Cyclic quadrilateral
Cyclic quadrilateral |
 Tangential quadrilateral
Tangential quadrilateral
|
|
|
Polygons
|
 Regular
polygons
Regular
polygons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Quadrilaterals |
| Square
|
| A
square is a plane figure with four sides of equal length and
four right angles. |
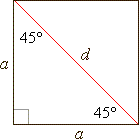
| The
two diagonals, which are of equal length, bisect each other
perpendicularly. |
| The
square has four axes of symmetry. |
|
 |
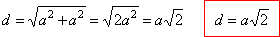 |
| perimeter
P
= 4a |
| area
A
= a ·
a = a2 |
A
= a2 |
|
|
|
|
| Rhombus
or rhomb
|
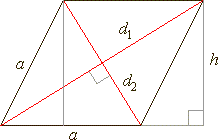
| A
rhombus is an oblique-angled parallelogram whose four sides are equal. |
| Rhombus
diagonals bisect each other perpendicularly. |
| The
rhombus is symmetrical about both of its diagonals. |
|
 |
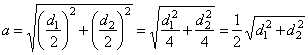 |
| perimeter
P
= 4a |
| area |
A
= a ·
h and |
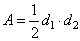 |
|
|
|
|
| Rectangle |
| A
rectangle is a plane figure with four straight sides, two parallel pairs
of equal length forming four right angles. |
| The two diagonals of
a rectangle have equal lengths. |
| The
rectangle has two axes of symmetry. |
|
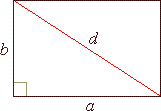 |
| diagonal |
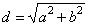 |
| perimeter
P
= 2(a + b) |
| area |
|
A
= a ·
b |
|
|
|
|
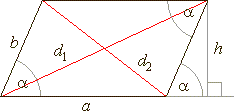
| Parallelogram |
| A
parallelogram
is a quadrilateral (plane figure with four sides) with opposite
sides parallel and of equal length. |
| The
opposite angles of a parallelogram are also equal. |
| In
the case in which the angles are all right angles the
parallelogram is a rectangle, and when all the sides are equal
it is a rhombus. |
|
 |
|
 |
| perimeter
P
= 2(a + b) |
| area |
|
A
= a ·
h |
|
|
|
|
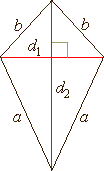
| Kite
or deltoid
|
| A
kite or deltoid is a quadrilateral with two pairs of equal
adjacent sides. |
| Two
of the angles in a kite are opposite and equal. |
| The kite's diagonals cross perpendicularly, and one of them (the shorter one) is being bisected by the other. |
|
 |
|
| perimeter
P
= 2(a + b) |
| area |
|
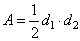 |
|
|
|
|
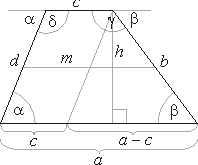
| Trapezium
or trapezoid
|
| A
trapezium or trapezoid is a quadrilateral with two parallel
sides of unequal length. |
| The trapezium's median is a straight line joining the midpoints of
nonparallel sides and parallel to the two parallel sides. |
|
 |
| a
+ d = 180°, b + g = 180° =>
a + b + g + d =
360° |
| median
m = 1/2(a +
c),
area |
A
= m ·
h |
| perimeter
P
= a + b + c + d |
| A
= c·h + 1/2(a -
c)·h =
1/2(a +
c)·h |
A
=1/2(a
+ c)·h |
|
|
|
| Isosceles
trapezoid
|
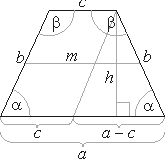
| A trapezoid with the two nonparallel sides of equal length and the angles opposite those sides equal, is called an isosceles trapezoid. |
 |
|
a
+ b = 180°, |
|
| median
m = 1/2(a +
c),
area |
A
= m ·
h |
| perimeter
P
= a + 2b
+ c |
| A
= c·h + 1/2(a -
c)·h =
1/2(a +
c)·h |
A
=1/2(a
+ c)·h |
|
|
|
| Cyclic quadrilateral |
| A
quadrilateral inscribed in a circle, so that all its vertices
lie on the circumference is called a cyclic
quadrilateral. |
| The
opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary. |
|
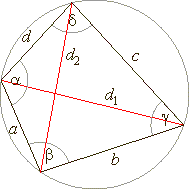 |
| a
+ g = b + d = 180°, |
| d1
· d2
= a · c + b
· d |
| perimeter
P
= a + b
+ c
+ d,
s
= 1/2P |
| area |
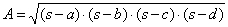 |
|
|
|
|
| Tangential quadrilateral
|
| A
quadrilateral whose sides all lie tangent to the circle
inscribed within the quadrilateral is called a tangential
quadrilateral. |
|
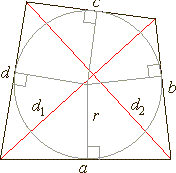 |
| s
= a +
c = b + d, |
| perimeter
P
= a + b
+ c
+ d, s
= 1/2P |
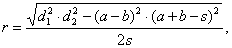 |
| area |
A
= r · s |
|
|
|
|
| Polygons
|
| A
polygon is closed plane figure
bounded by a number of straight line segments with the same
number of vertices. |
| The
sum of interior angles is (n
-
2) · 180°,
where n
is the number of sides of a polygon. |
| The
sum of exterior angles of a polygon is 360°. |
|
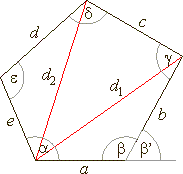 |
| dn
- number
of diagonals |
| b'
- the
exterior angle |
| dn
= 1/2 · n · (n
-
3) |
|
| Sn=
(n
-
2)
· 180° |
- the
sum of interior angles |
|
|
|
| Regular
polygons |
| In
a regular polygon all sides are equal and all its angles are
equal. |
| The
exterior angle of a regular polygon is b'
= 360°/n, where n
is the number of sides of a regular polygon. |
|
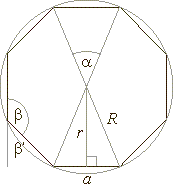 |
| a
=
b'
= 360°/n
|
b'
- the
exterior angle |
| b
=
180°
-
b'
= (n
-
2)
· 180°/n, |
P = n · a |
| dn
= 1/2 · n · (n
-
3) |
- number
of diagonals |
| A
= 1/2 · n · a · r
= 1/2P
· r |
-
area of a regular polygon |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Geometry
and use of trigonometry contents - A |
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |