|
| Integral
calculus |
|
|
|
The
indefinite integral |
 Trigonometric
integrals
Trigonometric
integrals
|
|
Trigonometric
integrals of the form
|
|
∫
sin (m x) sin (n x) dx,
∫
sin
(m x)
cos (n x)
dx,
∫
cos (m x)
cos (n x)
dx.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trigonometric
integrals of the form
|
|
∫
sin (m x) sin (n x) dx,
∫
sin
(m x)
cos (n x)
dx,
∫
cos(m x)
cos (n x)
dx,
|
|
in these cases we use the following product to sum formulas,
|
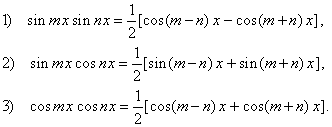
|
|
and the addition formulas.
|
|
|
|
|
|
We
can use the above formula 3) or derive it from the addition
formulas, thus
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Integrals
of rational functions containing sine and cosine, ∫
R
(sin x, cos x) dx
|
|
Integrals
of the form
|
|
∫
R
(sin x, cos x)
dx
|
|
where
R
denotes a rational function of sin
x
and cos
x,
can be transformed to a rational function of the new variable t,
using substitution tan
(x/2) = t. Then,
|
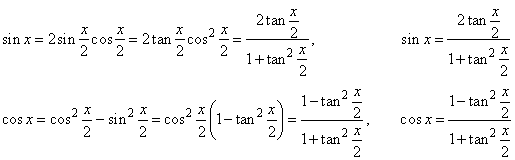
|
|
therefore,
by substituting
|
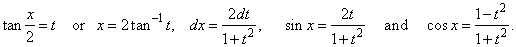
|
|
In
case the integrand expression does not change the sign when both
the sine and the cosine functions change
the sign, i.e., if
|
|
R
(-
sin x, -
cos x)
or
R
(sin x, cos x)
|
|
we
can use the substitution tan
x = t. Therefore,
|
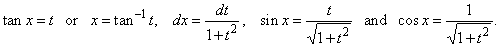
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Calculus contents
F |
|
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |