|
|
Applications of the derivative |
 Differential
of a function
Differential
of a function |
|
Rules
for differentials |
|
Differentials of some
basic functions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Differential
of a function |
| If
given y = f (x)
is differentiable function then, the derivative of y
or f (x) |
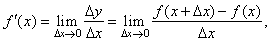 |
| as
the instantaneous rate of change of y
with respect to x,
can also be written as |
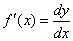 |
| where,
the increment
Dx
= dx is called differential of
the independent variable and dy
is the differential of y. |
| Therefore,
the differential of a function |
| dy
= f '(x) dx |
| represent
the main part of the increment Dy
which is linear concerning the increment Dx
= dx, as is shown in
the figure below. |
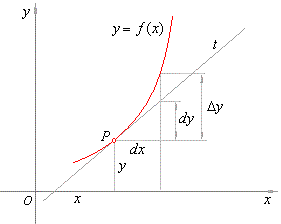 |
|
|
| Rules
for differentials |
| Rules
for differentials are the same to those for derivatives, such that |
|
1)
dc = 0,
c
is a constant |
|
2)
dx = Dx,
x
is the independent variable |
|
3)
d (cu) = c
du |
|
4)
d (u ±
v) = du ±
dv |
|
5)
d (u v) = u
dv ±
v du |
| 6) |
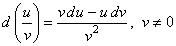 |
|
|
7) d
f (u) = f ' (u) du. |
|
|
Differentials
of some basic functions |
|
1) d
un = n
un -
1du |
|
2) d
eu = eu
du |
|
3)
d
an = an ln a
du |
| 4) |
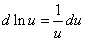 |
|
|
5) d
sin u = cos u
du |
|
6) d
cos u = -
sin u
du |
| 7) |
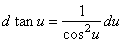 |
|
| 8) |
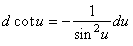 |
|
| 9) |
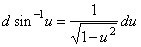 |
|
| 10) |
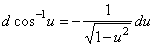 |
|
| 11) |
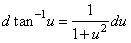 |
|
| 12) |
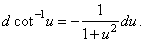 |
|
|
|
Example:
To
show the use of the formula 2) d
eu = eu du
above, let substitute;
a) u = x,
b) u = cos
x
and
c) u = x3.
|
|
Solution:
a)
By substituting u = x,
obtained is d
ex = ex dx
|
|
b) By substituting u =
cos x,
we get d
ecos x = ecos x
d(cos x) =
-
ecos x sin x
dx |
| |
c)
By substituting
u = x3,
we get |
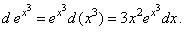 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Calculus contents
D |
|
 |
|
| Copyright
© 2004 - 2020, Nabla Ltd. All rights reserved. |
|
|